Question
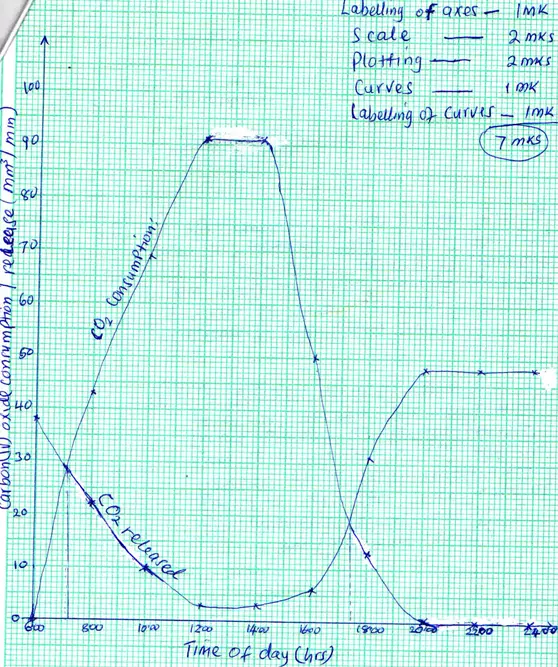
In an experiment to investigate a certain process in a given plant species, the rate of carbon (IV) oxide consumption and the rate of Carbon (IV) oxide release were measured over a period of time for the day. The results of the investigation are as shown in the table below
| Time of days(hrs) | 6.00 | 8.00 | 10.00 | 12.00 | 14.00 | 16.00 | 18.00 | 20.00 | 22.00 | 24.00 | CO2 consumption mm3/min | 0 | 43 | 69 | 91 | 50 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | CO2 release mm3/min | 38 | 22 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 31 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
|---|
(a) On the same axes, draw the graphs of volume of Carbon (IV) oxide consumed and Carbon (IV) oxide released against time
(b) Name biochemical processes represented by
(i) Carbon (IV) oxide consumption
(ii) Carbon (IV) oxide release
(c) Account for the shape of the curve for
(i) Carbon (IV) oxide consumption.
(ii) Carbon (IV) oxide release
(d) (i) From the graph, state the time of the day when the plant attains compensation point.
(ii) What is meant by compensation point.
(e) Explain how temperature affects the rate of Carbon (IV) Oxide consumption in a plant.
Answer
(b)
(i) Photosynthesis
(ii) Respiration
(i) CO2 consumption increases between 6.00 to 14.00 hrs ;increasing light intensity ;leads to an increase in the rate of photosynthesis, from 16.00 to 24.00, as light intensity decreases;
(ii) CO2 release decreases from 6.00 to 14.00 hrs, because it's being used in the process of photosynthesis.
From 16.00 to 24.00 CO2 release increases as it accumulates from process of respiration, since rate of photosynthesis is decreasing.
(i) 7.12 hrs ± 5 (7.07 - 7.17 ) and
17.24 hrs ± 5 (17.19 – 17.29)
(ii) The point where the rate of carbon (IV) oxide consumption (during photosynthesis) is equal to rate of carbon (iv)oxide release (during respiration);

