Question
The diagram below shows the transverse section of a young stem
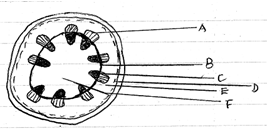
(a) What are the functions of the structures labeled A, B, C and D
A-
B-
C-
D-
(b) What type of cell are found in the part labeled E and F.
(c) If the shoot from which this section was obtained had been immersed in red coloured water for one hour, what part on the diagram would be stained
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in c (i) above
(d) Is this a monocot or a dicot stem? Give at least three reasons to support your answer

(a) What are the functions of the structures labeled A, B, C and D
A-
B-
C-
D-
(b) What type of cell are found in the part labeled E and F.
(c) If the shoot from which this section was obtained had been immersed in red coloured water for one hour, what part on the diagram would be stained
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in c (i) above
(d) Is this a monocot or a dicot stem? Give at least three reasons to support your answer
Answer
(a) A- Phloem:-Transport of organic food substances from their sites of manufacture, especially the leaves to other parts of the plant.
B- Cambium:-Formation of new xylem and phloem tissues or responsible for secondary growth.
C- Xylem:-Transport of water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves.
D- Epidermis:- Protects the inner, more delicate tissues from mechanical damage and from entry of pathogenic microorganisms.
(b) Parenchyma cells
(c) i) Part C would be stained
ii) Part C(Xylem) is responsible for transporting water and minerals.
(d) It is a dicot because of the following reasons:
- Parenchyma tissue is separated into cortex and pith.
-Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring between the cortex and pith.
-Vascular cambium is present.
B- Cambium:-Formation of new xylem and phloem tissues or responsible for secondary growth.
C- Xylem:-Transport of water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves.
D- Epidermis:- Protects the inner, more delicate tissues from mechanical damage and from entry of pathogenic microorganisms.
(b) Parenchyma cells
(c) i) Part C would be stained
ii) Part C(Xylem) is responsible for transporting water and minerals.
(d) It is a dicot because of the following reasons:
- Parenchyma tissue is separated into cortex and pith.
-Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring between the cortex and pith.
-Vascular cambium is present.

