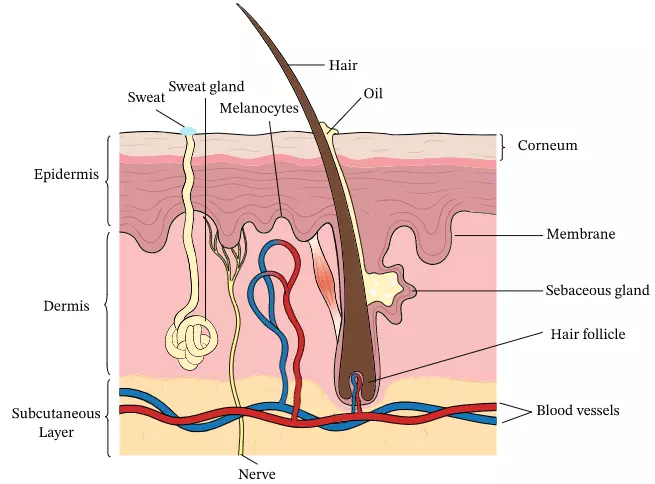
What is Reproduction?
- Reproduction is the process of giving rise to young ones (offspring) of the same kind.- The Male reproductive cell is known as a sperm (plural: sperms). It is produced in the testes.
- A female reproductive cell is known as an ovum (plural: ova). It is produced in the ovaries.
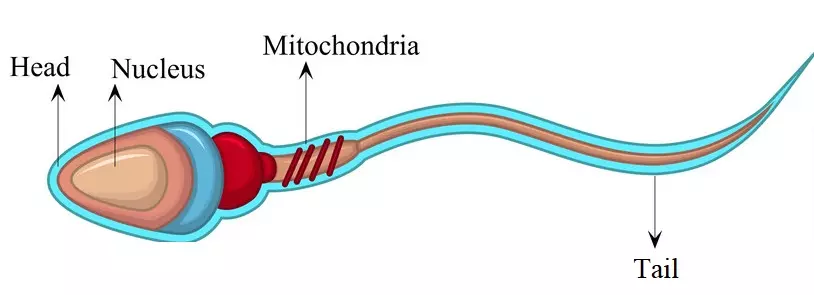
Sperm (plural: Sperms)
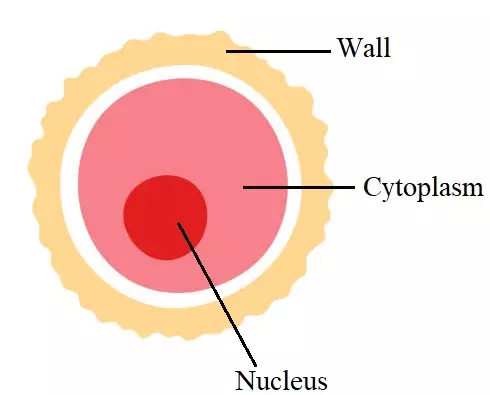
Ovum (plural: Ova)
Fertilization in Humans
- Fertilization is the union of a sperm cell and an ovum- During sexual intercourse, the penis (male organ) deposits sperms in the vagina (female organ)
- The sperms swim up to the fallopian tube (oviduct) via the uterus where they get to the ovum.
- Fusion process (where the sperm enters the ovum forming a zygote.
Development of the Foetus
- After fertilization, the sperm and the ovum form a single cell called a zygote.- The zygote undergoes cell division changing into a cell called an embryo.
- The embryo (which is a growing cell) moves down to the uterus (womb) developing fingerlike structures called placenta.
- The embryo attaches itself to the uterine wall in a process called implantation.
- The embryo then grows to become a foetus
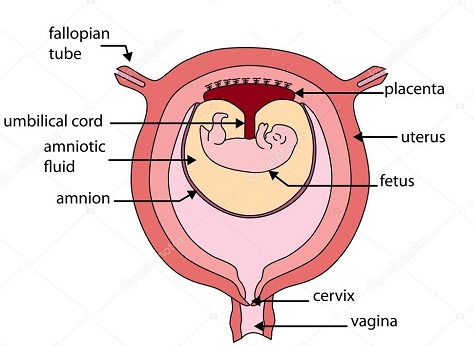
Parts of a the Uterus
Functions of the Placenta
- Facilitates production of necessary hormones to maintain the pregnancy- Enhances exchanges of oxygen from the mother's body to the foetus
- Enhances the exchange of carbon dioxide from the foetus to the mother's body
- Prevents disease-causing germs from reaching the foetus.
Functions of the umbilical cord
- Joins the placenta to the foetus- It passes oxygen and nutrients from the placenta to the foetus' bloodstream
- It passes carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes from the foetus to the placenta.
Amniotic fluid
- It is found within the amnion sac of the mother. - Functions of the amniotic fluid- Cushions the foetus from shock
- Allows easier foetal movement
- Controls the temperature to allow for safe growth of the foetus
- Lubricates the foetus
- Prevents dehydration by providing moisture.
The process of birth
(In humans the birth process occurs during the gestation period, usually 9 months)- The uterine wall contracts - also known as labour
- Following the contraction of the uterine wall, the amnion breaks, releasing fluids. The head of the foetus is pushed down the cervix
- Cervix enlarges (dilates) allowing the passage of the foetus down to the vagina
- The enlarged vagina allows the foetus, to come out, head first
- When the baby is out, the umbilical cord is tied and cut to separate the baby from the mother
- During afterbirth - part of the umbilical cord and placenta comes out