Question 1
Figure 1 shows a micrometer with a negative error of 0.02mm used to measure the diameter of a ball bearing.
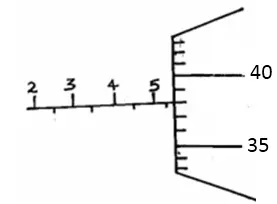
Record the diameter of the ball.
Answer

Question 2
An oil drop of volume 0.4mm3 was placed on a clean water surface. It spread to form a monoatomic circular patch of area 2000mm2. Use this data to calculate the diameter of a molecule of oil.
Answer
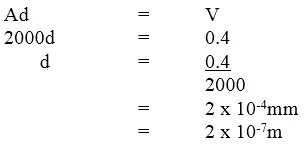
Question 3
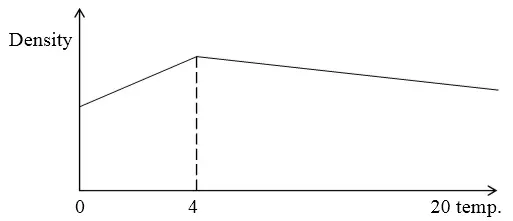
A fixed mass of pure water was cooled from 20°C to O°C. Sketch a graph of density of the water against temperature.
Answer
Question 4
Two 10g masses are fixed onto two similar aluminum plates, one polished and the other painted black, using wax as shown in the figure below.
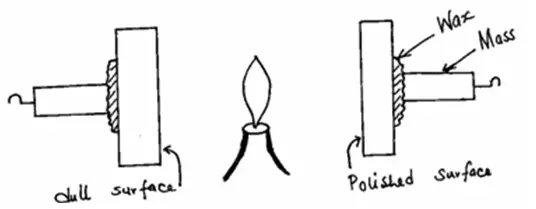
Give and explain the observation made.
Answer
- Mass on dull aluminum plates falls off before mass on polished aluminum plate.
- Dull aluminum absorbs heat faster than polished aluminum (it heats up faster and wax on it melts before)
- Dull aluminum absorbs heat faster than polished aluminum (it heats up faster and wax on it melts before)
Question 5
The figure below shows a charged leaf electroscope.
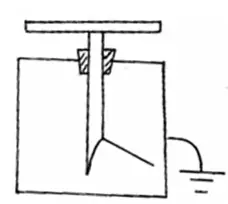
Given a dry glass rod and silk cloth, explain how you would determine the type of charge on the electroscope.
Answer
- Charge the glass rod by rubbing it with silk.
- Place the rod near the cap of the electroscope.
- If the divergence of the leaf increases, the electroscope is positive.
- If the divergence of the leaf decreases, the electroscope is negative.
- Place the rod near the cap of the electroscope.
- If the divergence of the leaf increases, the electroscope is positive.
- If the divergence of the leaf decreases, the electroscope is negative.
Question 6
State two advantages of alkaline accumulator over the lead-acid cell.
Answer
- It can give a bigger current.
- It can be left in the discharge condition for a long time without damage.
- It requires less attention.
- It is lighter.
- It can be left in the discharge condition for a long time without damage.
- It requires less attention.
- It is lighter.
Question 7
The figure below shows two magnets whose North poles are brought close to each other. Indicate the magnetic field pattern between the two magnets.

Answer
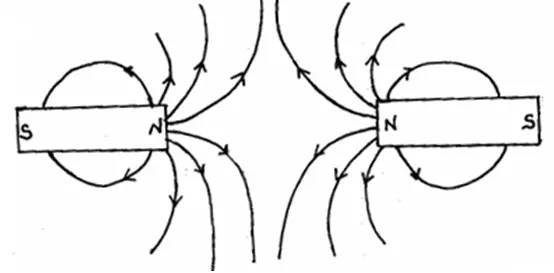
Question 8
The diagram shows a system in equilibrium with the uniform rule supported at Q and resting horizontally.
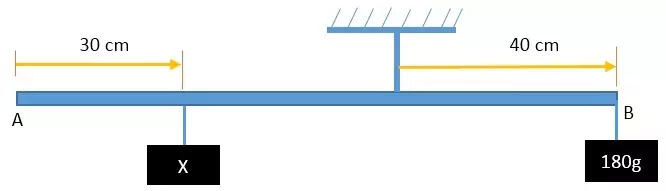
The rule is 1m long and weighs 1.8N. Calculate the weight of the block X.
Answer
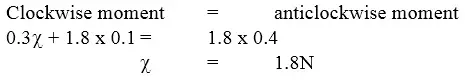
Question 9
An object is placed infront of a concave mirror as shown in the figure below. Complete the diagram to show how the image is formed.
Answer
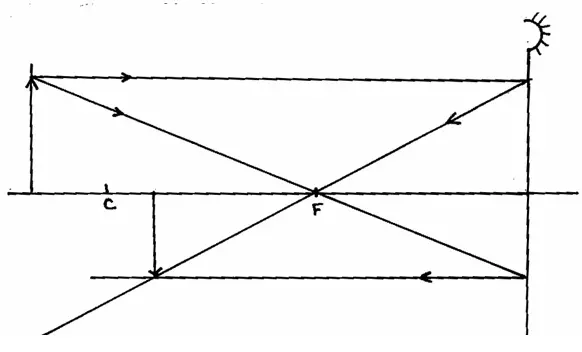
Question 10
State and explain what will happen to the freely suspended magnet when the switch S is closed.
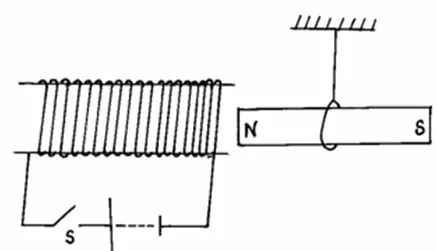
Answer
- Magnet will be repelled
- Coil is magnetized with end near magnet acquiring North Pole
- Coil is magnetized with end near magnet acquiring North Pole
Question 11
Three identical springs A, B and C are used to support a 15.5N weight as shown in the figure below.
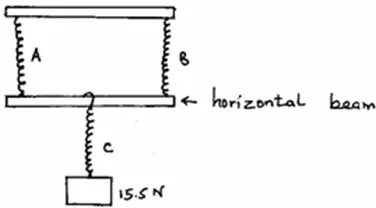
If the weight of the horizontal beam is 0.5N, determine the extension of each spring given that 4N cause an extension of 1cm when using one spring.
Answer
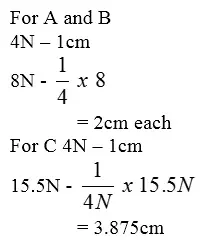
Question 12
State one of the major differences between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
Answer
- Mechanical waves require a material medium.
- Electromagnetic waves do not require a material medium.
- Electromagnetic waves do not require a material medium.
Question 13
A boat sent an ultrasound signal to the bottom of the sea and its echo received after 10 seconds. If the wavelength of the ultrasound in water is 0.05m and the frequency of the transmitter is 50 KHz, calculate the depth of the sea.
Answer
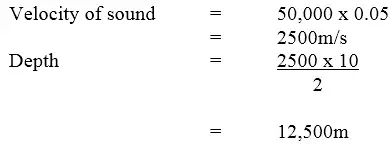
Section 2 Questions and Answers
Question 14
a) Complete the diagram below to show how an image is formed in a pinhole camera.
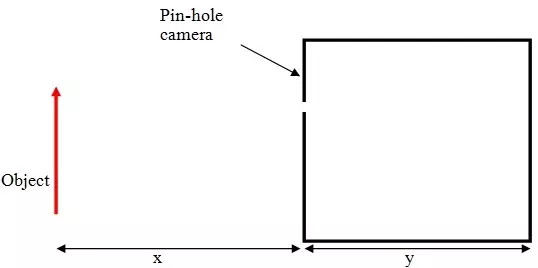
b) State two characteristics of the image above.
c) State two changes that will be observed about this image if the pinhole is made wider.
d) If x = 30cm, y = 12cm and the heights of the image is 4cm, calculate the height of the object.
Answer
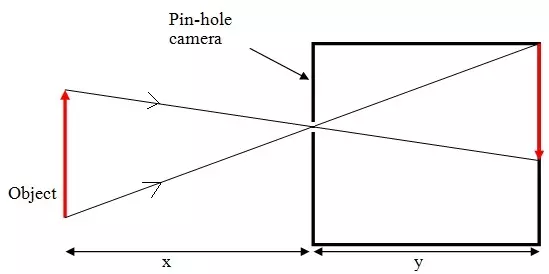
b) - Real
- Inverted
c) - Becomes brighter
- Becomes blurred
- Becomes bigger
d)
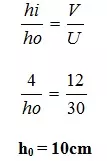
Question 15
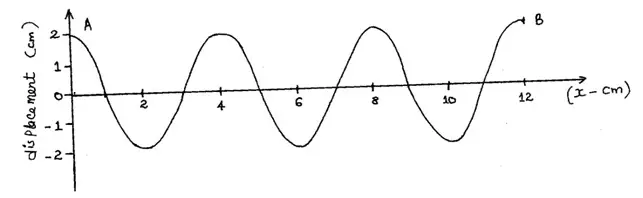
The diagram below shows the wave profile of a transverse wave.
(a) Determine
(i) the amplitude of the wave.
(ii) the wavelength of the wave in metres.
(iii) the period of the wave if it takes 1.5 seconds to move from A to B.
(b) Calculate:
(i) the frequency of the wave.
(ii) the velocity of the wave.
Answer
a)
(i) 2cm
(ii) 4cm = 0.04m
(iii)
3 oscli → 1.55
1 oscli → ?
Period = 1.55 ÷ 3
= 0.55
b)
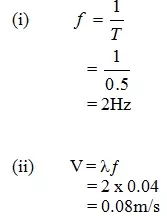
(i) 2cm
(ii) 4cm = 0.04m
(iii)
3 oscli → 1.55
1 oscli → ?
Period = 1.55 ÷ 3
= 0.55
b)
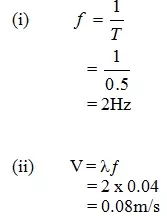
Question 16 - a
(a) What is diffusion?
Answer
It is the spreading of particles from regions of high concentration to those of low concentration.
Question 16 - b
(b) A smoke cell contain a mixture of trapped air and smoke. The cell is brightly lit and viewed through a microscope. State and explain what is observed.
Answer
- Bright specks are seen in continuous random motion.
- This is because of uneven bombardment by the invisible particles or molecules of air.
- This is because of uneven bombardment by the invisible particles or molecules of air.
Question 16 - c
(c) A beaker is filled completely with water. A spoonful of common salt is added slowly. The salt dissolves and the water does not overflow.
(i) State why the salt is added slowly.
(ii) Why doesn't the water overflow?
Answer
(i) To avoid splashing the water.
(ii) Because the salt particles fitted well in the spaces between the water molecules.
(ii) Because the salt particles fitted well in the spaces between the water molecules.
Question 16 - d
(d) In the figure below, ammonia gas and acid gas diffuse and react to form a white deposit on the walls of a long glass tube as shown.
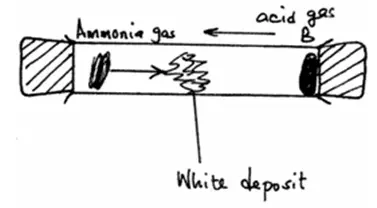
(i) What conclusion can be made from this result of this experiment?
(ii) How does the density of a gas affect the rate of diffusion?
(iii) The experiment is performed at a lower temperature. State and explain what would happen to the rate of diffusion of the gases.
Answer
(i) Ammonia gas diffuses at faster rate than hydrochloric acid gas.
(ii) A denser gas diffuses at a slower rate than the lighter one.
(iii) Diffusion takes longer time, because the particles are at low kinetic energy /moves slowly.
(ii) A denser gas diffuses at a slower rate than the lighter one.
(iii) Diffusion takes longer time, because the particles are at low kinetic energy /moves slowly.
Question 17 - a
(a) Give four differences between mass and weight.
Answer
| Mass | Weight |
|---|---|
| - Quantity of matter in a body | - Pull of gravity on a body. |
| - Measured in kilogram. | - Measured in Newton's. |
| - Same everywhere. | - Changes from place to place. |
| - Measured using a bean balance. | - Measured using a spring balance. |
| - Has magnitude only. | - Has both magnitude and direction |
Question 17 - b
(b) Sate Pascal's Principal.
Answer
Pressure applied at one part of a liquid is transmitted equally to all other parts of the enclosed liquid.
Question 17 - c
(c) Name two applications of Pascal's Principle.
Answer
(i) Hydraulic lift
(ii) Hydraulic brake system
(ii) Hydraulic brake system
Question 17 - d
(d) Figure 3 shows a U-tube containing two liquids L1 and L2 of densities 1.6g/cm3 and 0.8g/cm3 respectively in equilibrium.
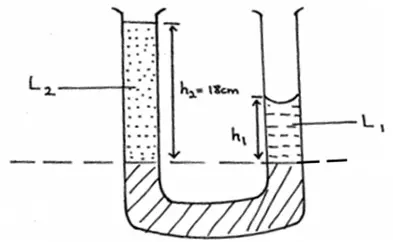
Given that h2 = 18cm, determine the value of h1.
Answer
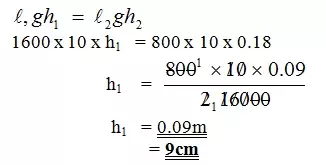
- End of Questions -
