The reaction of metals with water depends on the reactivity series.
The higher the metal in the reactivity series the more reactive the metal with water
Reaction of Sodium/Potassium with Cold Water
An experiment is conducted as follows;- Put about 500cm3 of water in a beaker
- Add three drops of phenolphthalein indicator into the water
- Cut a very small piece of sodium and put the metal into the water using a pair of forceps
NOTES
- Sodium melts to a silvery ball that floats and darts on the surface decreasing in size
- Effervescence/fizzing/ bubbles of colourless gas produced
- Colour of phenolphthalein turns pink
- Sodium is less dense than water, hence floats on water
- Sodium vigorously reacts with water to form an alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide and producing hydrogen gas
- Sodium is stored in paraffin to prevent contact with water
Sodium + Water
 Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas
Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas2Na(s) + 2H2O (l)
 2NaOH (aq) + H2 (g)
2NaOH (aq) + H2 (g)- Potassium is more reactive than Sodium
- On contact with water it explodes/burst into flames
- An alkaline solution of potassium hydroxide is formed and hydrogen gas
Potassium + Water
 Potassium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas
Potassium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas2K(s) + 2H2O (l)
 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)Reaction of Lithium/Calcium with Cold Water
An experiment is conducted as follows;- Put about 200cm3 of water in a beaker
- Add three drops of phenolphthalein indicator into the water
- Cut a small piece of Lithium and put the metal into the water using forceps
- Repeat with a piece Calcium metal
NOTES
- Lithium sinks to the bottom of the water and rapid effervescence/fizzing/ bubbles of colourless gas produced
- Colour of phenolphthalein turns pink
- Lithium and calcium are denser than water.
- Both sink in water and vigorously react to form an alkaline solution and produce hydrogen gas.
- Lithium is more reactive than calcium and is also paraffin like Sodium to prevent contact with water
- The following equations are representative of the reactions that occur
Lithium + Water
 Lithium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas
Lithium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas2Li(s) + 2H2O (l)
 2LiOH (aq) + H2(g)
2LiOH (aq) + H2(g)Calcium + Water
 Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas
Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas Ca(s) + 2H2O (l)
 Ca (OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Ca (OH)2(aq) + H2(g)Reaction of Magnesium/Zinc/Iron with Steam/water vapour
An experiment is conducted as follows;- Place some wet sand or cotton/glass wool soaked in water at the bottom of an ignition/hard glass boiling tube
- Polish magnesium ribbon using sand paper
- Coil it at the centre of the ignition/hard glass boiling tube.
- Set up the apparatus as below
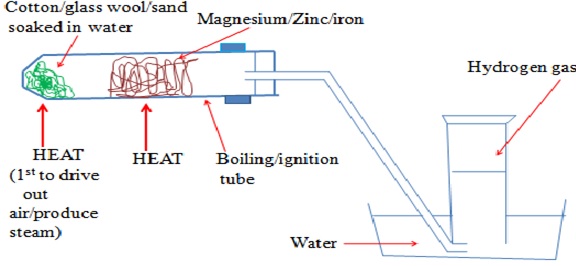
- Heat the coiled ribbon strongly using another burner
- Repeat the experiment using Zinc powder and fresh Iron filings
A. Reaction with Magnesium
The Magnesium glows with a bright flame. It continues to burn even if heating is stopped. White solid /ash that dissolve in water to form a colourless solution is formed. Colourless gas produced/collected that extinguish burning splint with “pop sound”
- Hot magnesium burn vigorously in steam
- The reaction is highly exothermic generating enough heat/energy to proceed without further heating
- White Magnesium oxide solid/ash is left as residue
- Hydrogen gas is produced and extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound
Magnesium + Steam Magnesium oxide + Hydrogen
Magnesium oxide + Hydrogen
Mg(s) + H2O(g) MgO(s) + H2(g)
MgO(s) + H2(g)
- Magnesium oxide reacts /dissolves in water to form an alkaline solution of Magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide + Water Magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxide
MgO(s) + H2O(l) Mg(OH)2(aq)
Mg(OH)2(aq)
- The reaction is highly exothermic generating enough heat/energy to proceed without further heating
- White Magnesium oxide solid/ash is left as residue
- Hydrogen gas is produced and extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound
Magnesium + Steam
 Magnesium oxide + Hydrogen
Magnesium oxide + HydrogenMg(s) + H2O(g)
 MgO(s) + H2(g)
MgO(s) + H2(g)- Magnesium oxide reacts /dissolves in water to form an alkaline solution of Magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide + Water
 Magnesium hydroxide
Magnesium hydroxideMgO(s) + H2O(l)
 Mg(OH)2(aq)
Mg(OH)2(aq)B. Reaction with Zinc Powder
The Zinc powder turns red hot on strong heating. Yellow solid formed that turn white on cooling. White solid formed on cooling does not dissolve in water.
- Hot Zinc react vigorously in steam forming yellow Zinc oxide solid/ash as residue which cools to white
- Hydrogen gas is produced and extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound
Zinc + Steam Zinc oxide + Hydrogen
Zinc oxide + Hydrogen
Zn(s) + H2O(g) ZnO(s) + H2(g)
ZnO(s) + H2(g)
- Zinc oxide does not dissolve in water
- Hydrogen gas is produced and extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound
Zinc + Steam
 Zinc oxide + Hydrogen
Zinc oxide + HydrogenZn(s) + H2O(g)
 ZnO(s) + H2(g)
ZnO(s) + H2(g)- Zinc oxide does not dissolve in water
C. Reaction with Iron Fillings
The Iron fillings turn red hot on strong heating. Dark blue solid formed. The dark blue solid formed does not dissolve in water.
- Hot Iron reacts with steam forming dark blue tri iron tetra oxide solid/ash as residue
- Hydrogen gas is produced and extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound
Iron + Steam Tri iron tetra oxide + Hydrogen
Tri iron tetra oxide + Hydrogen
2Fe(s) + 4H2O(g Fe2O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Fe2O4(s) + 4H2(g)
- Hydrogen gas is produced and extinguishes a burning splint with a pop sound
Iron + Steam
 Tri iron tetra oxide + Hydrogen
Tri iron tetra oxide + Hydrogen2Fe(s) + 4H2O(g
 Fe2O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Fe2O4(s) + 4H2(g)



