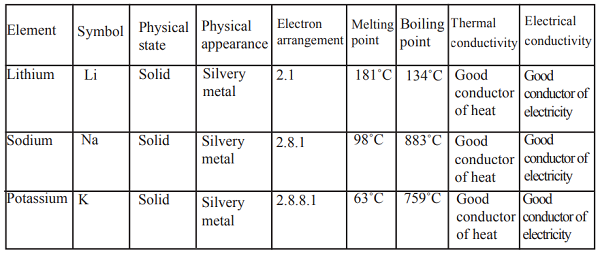
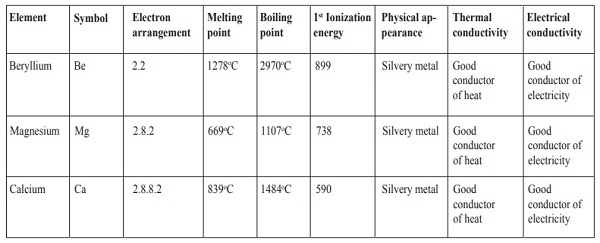
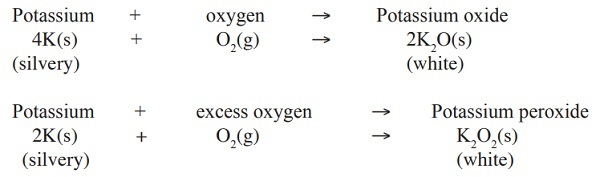Generally, alkaline-earth metals burn in air to form simple metal oxides.
1. Beryllium
Beryllium is a silvery metal. It has a very strong but very thin layer of beryllium oxide on its surface which prevents any further attack from air. In fact getting to the underlying beryllium to react with air is very difficult even at over 600
oC. However, powdered beryllium metal does burn in air to give a white beryllium oxide.
Beryllium + Oxygen → Beryllium oxide
2Be(s) + 2O2(l) → 2BeO(aq)
2. Magnesium
Magnesium burns readily with an intense bright white flame to produce a white powder of magnesium oxide.
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide
2Mg(s) + 2O2(l) → 2MgO(aq)
3. Calcium
Calcium is a silvery metal. The surface of the calcium metal is covered with a thin layer of oxide that protects the metal from further attack by air. At first it is reluctant to burn because of the oxide coating, but then bursts drastically into a white flame, which burns intensely to form a white solid of calcium oxide
Calcium + Oxygen → Calcium oxide
2Ca(s) + 2O2(l) → 2CaO(aq)
NOTE: Beryllium, magnesium and calcium
do not form peroxides when heated in air. The
reactivity increases as you go down the group due to increasing ease of removing the electrons in the outermost energy level.
Reaction of Alkaline-earth metals (Mg and Ca) with Water
Beryllium does not react with water or steam even when it is red-hot.
Very clean
magnesium slightly reacts with cold water to form magnesium hydroxide solution which turns red litmus blue and hydrogen gas
Magnesium + water → magnesium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Mg(s) + 2H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Calcium reacts with cold water with increased vigour than magnesium to give calcium hydroxide solution and hydrogen gas.
Calcium + water → Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
NOTE: The reactivity of alkaline-earth metals with water shows
increasing reactivity as you go down the group. This is mainly due to decreasing ionization energy down the group.
Reaction of Alkaline-earth metals (Mg and Ca) with Chlorine
Alkaline-earth metals react with chlorine to form chloride salts.
Heated beryllium metal reacts with chlorine to form beryllium chloride.
Beryllium + Chlorine → Beryllium chloride
Be(s) + Cl2(l) → BeCl2(aq)
Magnesium burns in chlorine with a bright light to form a white solid of magnesium chloride.
Magnesium + Chlorine → Magnesium chloride
Mg(s) + Cl2(l) → MgCl2(aq)
Calcium appears to burn slowly in chlorine compared to magnesium to form a white solid of calcium chloride.
Calcium + Chlorine → Calcium chloride
Ca(s) + Cl2(l) → CaCl2(aq)
Reactivity of alkaline-earth metals with chlorine
increases as you go down the group.
The calcium oxide coating formed on the surface as a result of its reactivity with oxygen forms a protective coat that make the reaction of calcium to appear slower. The inner silvery calcium metal cannot be easily reached by the chlorine.
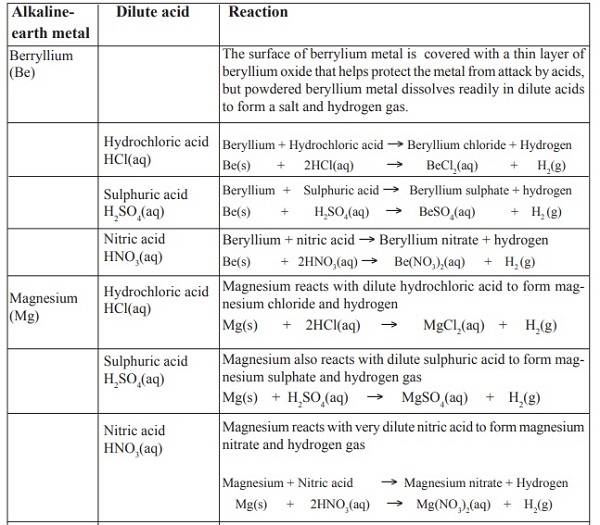
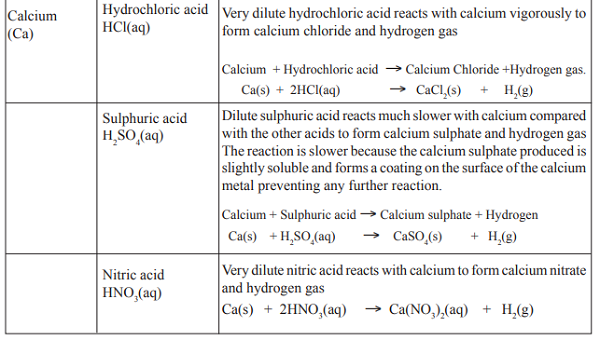
Reaction of alkaline-earth metals with dilute acids
Reaction of calcium and acids is very explosive. Very dilute acids should be used. Alkaline-earth metals
react with dilute acids to form a salt and hydrogen only. The evolution of hydrogen gas is evident by the
'pop' sound produced by the burning splint. Very dilute nitric acid should also be used with magnesium.
Uses of Alkaline-earth Metals
(a) Beryllium
- Used in transmission of X-rays (beryllium transmits X-rays better than aluminium).
- Beryllium alloyed with copper gives a hard strong alloy with high resistance to wear. It is therefore used in computer parts, and other instruments with desirable lightness and stiffness.
- Alloys of beryllium are used as structural materials for high performance aircrafts, missiles, spacecraft and communication satellites among many other things.
- The oxide is used in the nuclear industry.
(b) Magnesium
- It is lighter than aluminium, and it is used to make alloys used for aircraft, car engine casings, and missile construction.
- It is used as a reducing agent for the production of uranium and other metals from their salts.
- Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia), chloride, sulphate (Epsom salts), among others are used in medicine.
- Magnesium oxide is used as brick-liners in furnaces.
- Used in computers for radio-frequency shielding.
(c) Calcium
- It is used as a reducing agent in the preparation of metals such as thorium, uranium, zirconium, etc.
- Calcium forms calcium carbonate which is a component of Portland cement.
- Calcium carbonate is used as antacid tablets.