Definitions
- Weather can be defined as the state of atmosphere of a particular place and time (usually 24 hours) in regards to heat, cloudiness, sunshine, wind, rain and more.- Climate is the weather conditions of an area in general over a long period of time, usually 30-35 years.
- Vegetation are the plants collectively found in a particular habitat.
Weather
Traditional Methods of Observing Weather
- Since our ancestors, weather has been a vital aspect of our lives. Here are some ways traditional people used to observe weather- Migration of birds and insects: Birds and insects migrate to avoid bird weather such as extreme heavy rainfall.
- Presence of dew. - dew in the morning signifies likelihood of no rain during the day
- Speed and direction of wind
- Shedding of leaves of some trees
- Appearance of certain clouds in the sky

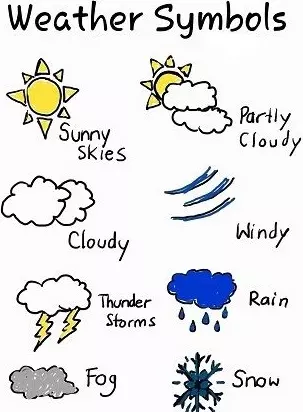
- Here are the main types of weather symbols you will come across in your studies
Observation, Measurement, Recording of Elements of Weather
a) Temperature
- Degree of hotness or coldness of an object or a place- It is measured using a thermometer
- The units for measuring temperature are Degrees Centigrade (°C)

A simple thermometer shown above
Did you know the main types of thermometer? We have a simple thermometer (shown above) and a Six's maximum and minimum thermometer. A simple thermometer has only mercury while a Six's maximum and minimum thermometer has mercury (shows maximum temperature) and alcohol (shows minimum temperature).
b) Rainfall
- Rainfall can be defined as the amount of water that falls from the sky.- It is usually measured using a rain gauge
- The units of measurement are Millimeters (mm)
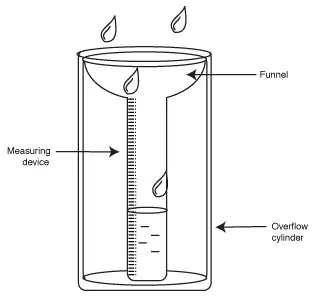
This is a rain gauge
c) Wind
- Wind can be defined as moving air.- Usually, wind is described in terms of direction, strength and speed.
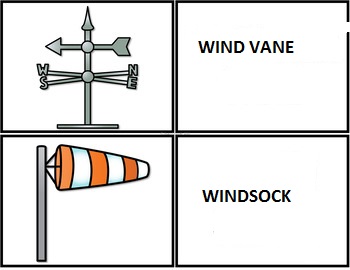
- The Wind direction is measured using both the windsock and a wind vane
- An anemometer is used to measure the speed of wind.

d) Air Pressure
- The is the pressure exerted on earth by air. (Atmospheric Pressure)- It is measured using a Barometer
- It is measured in Millimeters of Mercury (mmHg) or Millibars
Below is a simple barometer that is used in experiments in schools
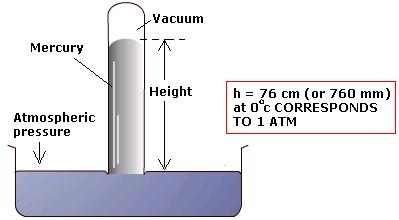
A simple barometer
e) Humidity
- it is defined as the amount of water vapour in the air- it is measured using a hygrometer
- the unit of measurement is percentage (%)
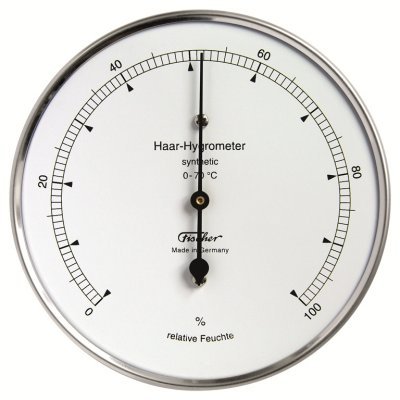

A hygrometer
Due to their sensitivity, a hygrometer and a thermometer are placed inside a Stevenson's screen in a weather station.
Climate
Climate can be described as:- Hot and Wet: has high temperatures and high rainfall (equatorial climate)
- Cool and Wet: has low temperatures and high rainfall (Mountain Climate)
- Hot and Dry: has high temperatures and low rainfall (desert and semi-desert climates)
- Equatorial climate, Savannah climate, Mediterranean climate, Mountain climate, Desert and Semi-desert climate are the main climates experienced in almost all regions in Africa.
Vegetation
- Vegetation refers to the different plants found in a place or habitat.- Natural vegetation is the plant cover that grows in a place under natural conditions.
- Vegetation is mainly influenced by the climate of the region
- Equatorial rain forest (Tropical rain forest), Tropical Savannah climate, Mediterranean vegetation, Mountain vegetation, Temperate grasslands, Desert and Semi-desert vegetation are the main vegetations found in Africa.



