Key Components on a Map
The main components of a map are
Title
- Always check for the title at the top of the map
- The title describes what the map is all about and gives a summary of the map.
Key
- Every map has symbols which represent physical and man-made features on a map.
- A key describes these features.
Compass
- A compass helps find direction of features in relation to others.
Frame
- The boundary of a map is the frame which makes it more compact.
Scale
- A scale is a representation of the actual distances between features on a map
- A map can have one of three different types of scales: They are:
a) Linear scale
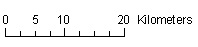 b) Statement Scale
b) Statement Scale: e.g
1cm rep 3km
c) Representative fraction e.g
1/10,000. It is also known as ratio scale.
Features on a Map
- Several features are usually represented on a map.
Man-made features
There are several man-made features that can exist on a map.
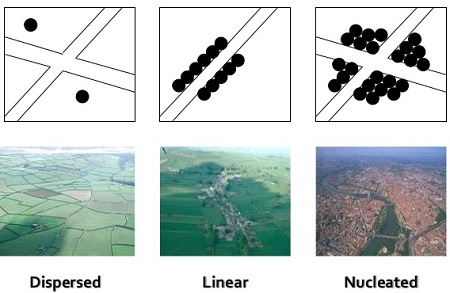
a) Human Settlements
Human settlements can be Linear, Clustered or sparse.
b) Economic Activities
- There are many economic activities that ca exist on a map
- Some of them are:
-
Fishing : presence of fish processing plants and fishing traps
-
Tourism : presence of museums, game and national parks
-
Livestock Rearing: presence of cattle dips and water holes, presence of cattle ranches, meat and milk processing factories
-
Mining - presence of quarries and mineral processing plants
-
Lumbering - Presence of saw mills
-
Trading - presence of markets and trade centres
-
Transport and communication - presence of roads and communication lines
-
Crop farming - presence of irrigation schemes, farming estates and more.
Determine the Climatic Conditions of a Map
The climate on a map can de identified as either
1) Cool and wet - presence of crops such as tea and coffee, rearing of dairy cattle is done and the evidence of a highland relief.
2) Hot and Wet - presence of crops such as sugarcane, rice and cotton, evidence of natural forests
3) Hot and Dry - presence of crops such as sisal, seasonal rivers and lakes, scanty vegetation as well as presence of boreholes.
Measuring distances and Calculating areas of regions
a) Using a Piece of Paper
On a map, take a piece of paper and mark a starting point. Follow the feature such as road you are measuring and mark points on the piece of paper that are straight. Check the diagram below.
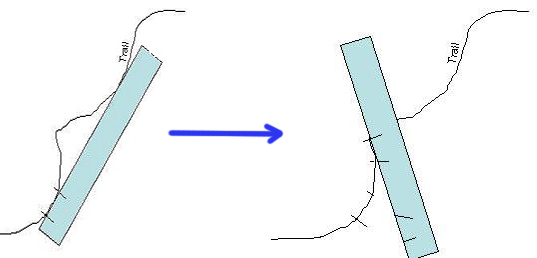
Place the marked piece of paper on the scale to get the measurement.
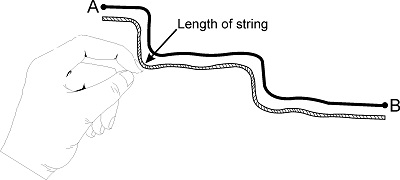
b) Using a String
Using a string, follow the road you are measuring from the starting point to the end point. On the string, mark both points. Thereafter, place the piece of string from the start point to measure the distance.
Calculating area
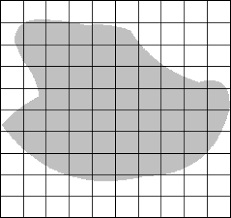
- When calculating the area of a regular shape, measure the length and width and multiply both to get the area.
- For an irregular shape, it will be take more activity. Draw 1cm by 1cm squares over the irregular shape. Calculate the number of complete squares and the number of incomplete squares.
- Divide the number of incomplete squares by 2. Thereafter, sum up the two. The result is the area.
Determining the Direction
Direction of one feature from the other can be determined by:
a. Draw a line between the two points.
b. Draw a compass on the point you are telling the direction from while using the direction of North on the compass provided on the map.
c. Read the direction.
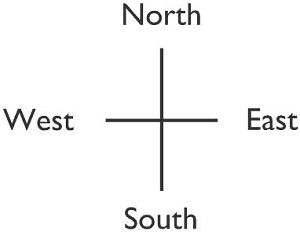
The four main directions are:
- North (N)
- East (E)
- South (S)
- West (W)
- The diagram below shows a simple compass:
Sloping of Land
- The direction of flow of a river determines the direction which the land on the map is slopping.
- Observe river sources, crops grown as well as human settlements to determine high areas of a map.





