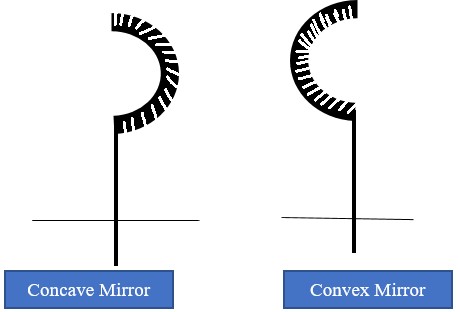
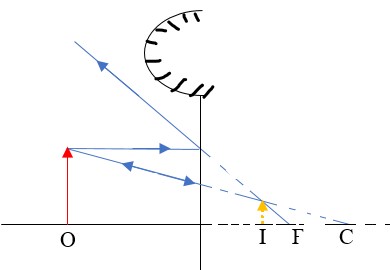
-If the inside is silvered a convex or diverging is formed while a concave or converging mirror is formed when the outside is silvered.
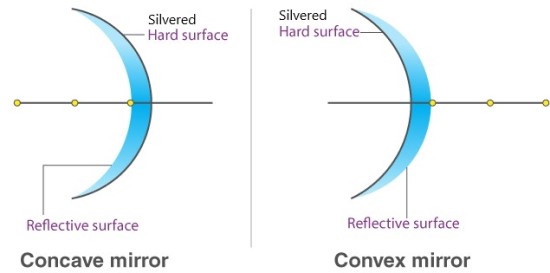
Parts of a Spherical Mirror
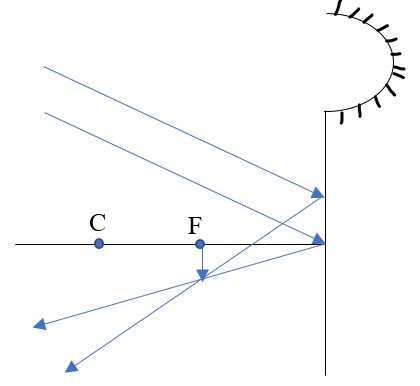
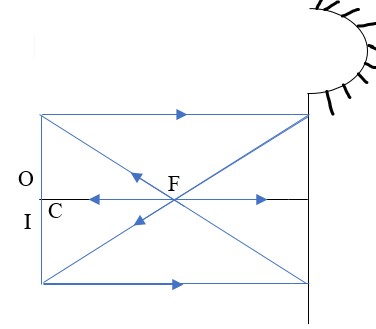
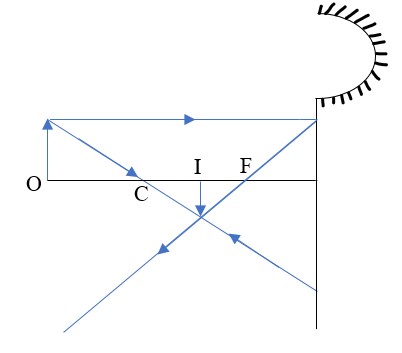
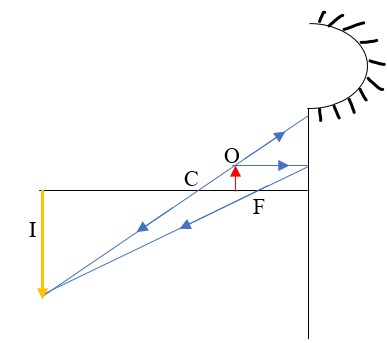
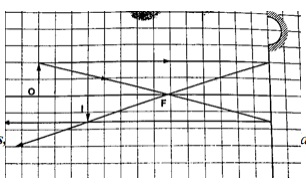
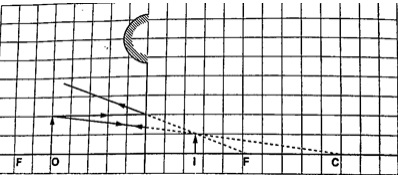
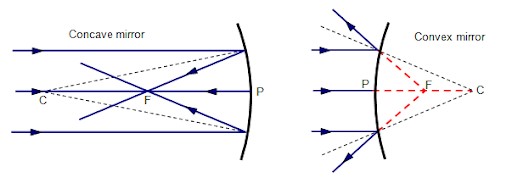
- Centre of curvature (C) – this is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is part of. The centre itself is called the pole (P).
- Principal axis – this is the line joining the centre of curvature (C) to the pole (P).
- Principal focus (F) – is a point on the principal axis through which a ray is reflected when it hits a concave mirror. In a convex mirror the ray is reflected and appears to originate from the point. F is virtual for a convex mirror while it is real for a concave mirror.
- Radius of curvature (r) - this is the distance from the pole to the centre of curvature. The distance from the pole to the principal focus is called the focal length (f).
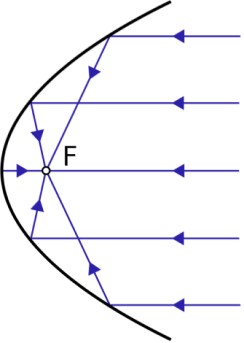
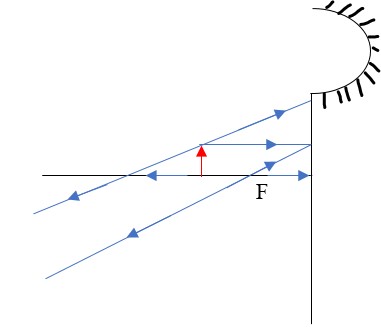
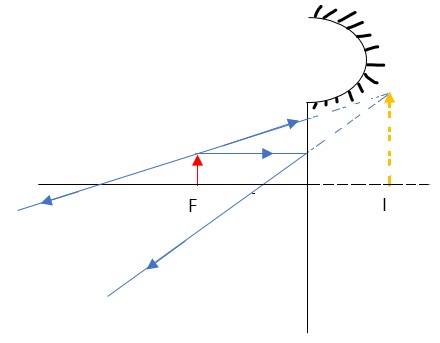
Parabolic Mirrors
- They produce a wide parallel beam or converge a large beam of light to a point.- They are widely used in making car headlights or in spotlights.