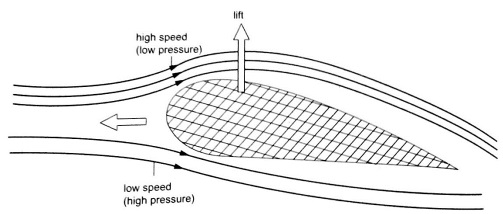
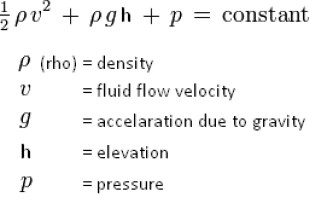- We consider fluids to be incompressible
- We assume that they have little or no internal friction or viscosity
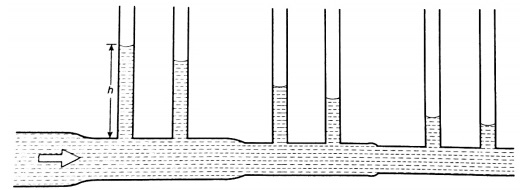
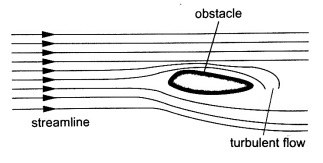
Streamline and Turbulent Flow
- The path followed by a small element of a moving fluid is called a line of flow.- A streamline is a curve whose tangent at any point is in the direction of the fluid velocity at that point.
A streamline flow occurs when all elements of a fluid passing a particular point follow the same path or line of flow as the elements that passed through that point previously.
- A streamline flow is achieved only when the speed is low.
- Turbulent flow generally occurs when the speed is high and where there are sharp bends along the path of the fluid.
Equation of continuity
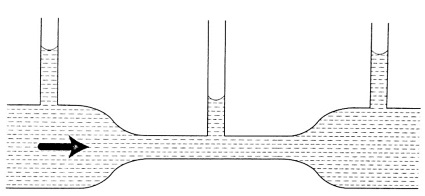
- Consider a fluid flowing (streamline flow) through a horizontal pipe with different cross-sectional areas as shown.
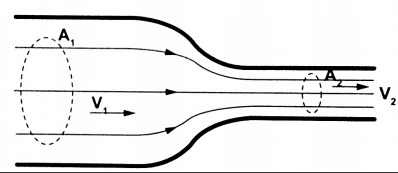
- The volume of fluid flowing per second in each section is given by;
V = A L = A v t = A v. Where L, v t and v is the distance moved in one second.
- Since the volumes in each section is the same, then,
A1 V1 = A2 V2, hence A v = constant.
- The above equation is known as the equation of continuity.
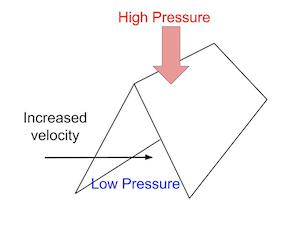
Since A1 > A2, then V2 > V1. i.e. the speed increases when a tube narrows.
- The quantity (A v) is called volume efflux i.e. volume flowing per second.
Practice Example 1
A horizontal pipe of cross-sectional area 50 cm2 carries water at the rate of 0.20 litres per second. Determine the speed:a) Of the speed of water in the pipe.
b) When the tube narrows to 20 cm2 at another point.
Solution
a) Volume efflux = 0.20 l per second = A vFrom V (volume) = A v, then v = V / A = 0.20 × 10-3 / 50 x 10-4 = 0.04 m/s.
b) Since A1/v1 = A2/v2 then v2 = (0.05 x 0.04) / 0.02 = 0.1 m/s.