Question 1
- What is the relationship between Geography and Chemistry
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth
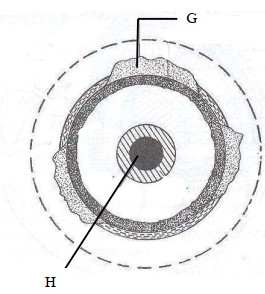
(i) Name the parts marked G and H.
(ii) Name the dominant mineral in the mantle.
Answer
-
- Geography applies Chemistry concepts in studying the chemical composition of rocks and soils.
- Chemistry concepts are used in Geography to explain chemical changes that occur in rocks/soils -
(i)
G - Continental crust/sial
H - Inner core
(ii) - Olivine/ ferromagnesian silicate
Question 2
Differentiate between absolute and relative humidity
Answer
- Absolute humidity is the actual amount of water vapour or moisture in a given mass of air at a particular temperature while relative humidity is the ratio of the absolute humidity of a given mass of air to the maximum amount of moisture that this mass of air could hold at the same temperature
- The amount of water vapour determines the amount of energy stored in the atmosphere for the development of storms.
- The amount of water vapour determines the amount of energy stored in the atmosphere for the development of storms.
Question 3
The diagram below shows some features formed by faulting.

- Name the parts marked X and Y.
- State three effects of faulting on drainage of an area
Answer
-
X - Hade
Y - Fault scarp/escarpment/scarp face -
- Down warping due to faulting may lead to formation of depressions which may be filled by water to form lakes.
- Fault lines due to fracturing of crustal rocks may change the course of river making the river to start flowing a long the fault line forming faulting - guided drainage pattern.
- Fault scarps forming across rivers course may lead to formation of waterfalls.
Question 4
- Identify two scales used to measure the intensity of an earthquake
- Give three major earthquake zones of the world
- Explain three economic significance of rocks in Kenya
-
Students carried out a field study on rocks around their school
(i) State two importance of stating the objectives for the study
(ii) Give three reasons why they prepared a route map of the study area
Give three activities that the students where involved in during the field study
Answer
-
- Rossi forell scale
- Mercalli scale -
- The mid-Atlantic
- The Great Rift Valley region
- The Mediterranean region/Tethyan -
- Some rocks such as granite, volcanic peaks may form unique sceneries which attract tourists promoting tourism industry.
- Rocks provide the parent materials through weathered rocks especially volcanic rocks forming fertile volcanic soils for agricultural production.
- Rocks such as sandstone, marble and limestone are strong and resistant to weathering are used in the building and construction industry. -
(i)
- They direct the actual activities to be carried out during the study.
- They guide the possible areas of data collection to obtain required information.
(ii)
- To identify direction they would take
- To show the features/rocks they are likely to see.
- To help estimate the distance to be carried
(iii)
- Data collection/taking photographs/filming/videoing
- Data recording/ taking notes/tallying/sketching
- Collecting different types of rock samples.
Question 5
-
(i) What is an orogeny?
(ii) Give two factors that influence the folding process of rocks -
The diagram below shows some types of folds. Use it to answer the question

(i) Name the types of folds marked E and F
(ii) Describe how an overthrust fold is formed -
Name the countries in which the following fold mountains are found
(i) Atlas
(ii) Alps
(iii) Himalayas
(iv) Andes
-
(i) Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding.
(ii) Explain four ways in which fold mountains influence climate
Answer
-
(i) - A fold mountain building period.
(ii) - The strength/intensity/magnitude of the compressional forces.
- The nature of the sedimentary rocks/The age of the rocks -
(i) E - Overfold
F - Recumbent fold
(ii) - Layers of rocks of the earth’s crust are subjected to compressional forces.
- Intense folding result in the formation of an overfold.
- With increased pressure, the overfold results in the formation of recumbent fold producing a thrust plane.
- The upper part of the recumbent fold slides forward over the lower part along the fault plane resulting to the formation of an overthrust fold. -
(i) - Western Sahara
- Morocco
- Algeria
(ii) - Austria
- Switzerland
- Italy
- France
- Leichstein.
(iii) - India
- Pakistan
- Afghanistan
- Bhutan
- Nepal
- China
(iv) - Chile
- Peru
- Bolivia
- Argentina
- Venezuela
- Ecuador
- Colombia
-
(i) - Synclinal valleys/depressions
- Rolling plains
- Ridges
(ii)- The slopes of mountains which face the sun receive direct sunshine and are warmer.
- Mountain slopes cause the development of local winds due to variation in pressure between the mountain top and the valley bottom.
- The windward slopes of mountains receive high rainfall due to orographic effect.
- Atmospheric pressure reduces with increasing attitude along a mountain slope.
