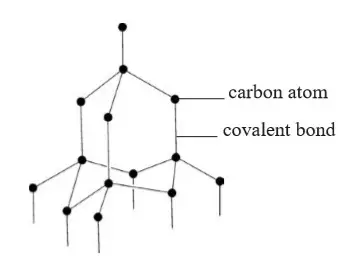
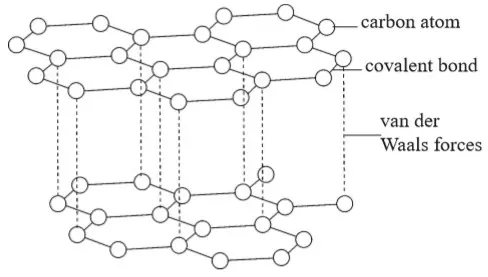
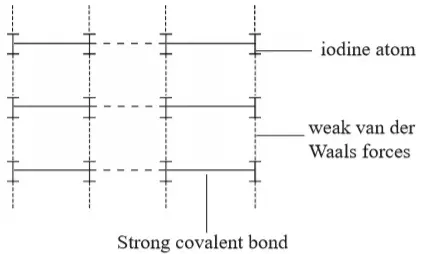
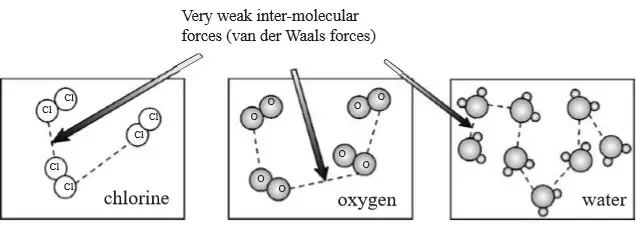
1. Ionic Chemical Bonding
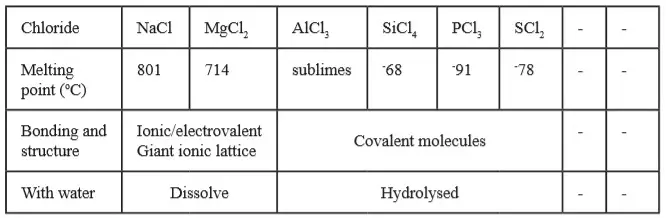
- Consider a specific case of ionic bonding between real elements, such as sodium and chlorine.- A sodium atom contains 11 protons and has an electronic arrangement of 2.8.1.
- The arrangement differs from the nearest noble gas electronic structure, that of neon, 2.8 by the presence of one extra electron in the third energy level.
- On the other hand, a chlorine atom contains 17 protons and has the electronic arrangement of 2.8.7.
- It differs from the nearest noble gas electronic arrangement, that of argon, 2.8.8, by missing one electron in the third energy level.
- In order to attain the stable noble gas electron arrangement, a sodium atom would have to lose the electron in the outermost energy level.
- The chlorine atom would need to take one electron into its outer energy level to gain the noble gas structure.
- During ionic chemical bonding of sodium and chlorine atoms, the single electron from the outermost energy level of sodium atom is transferred to the outermost energy level of the chlorine as shown in Figure 1 below.
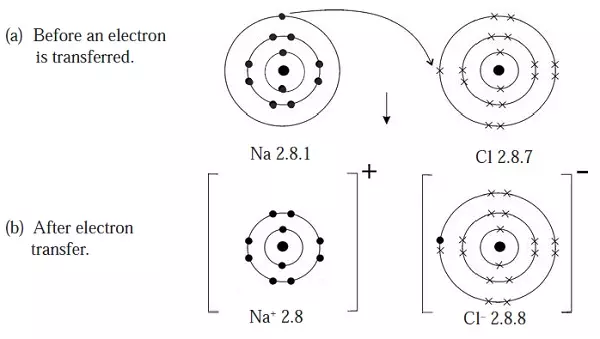
Figure 1: Ionic bonding in sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Sodium atom has 11 positive charges (protons) balanced by 11 negative charges (electrons).
- Sodium ion has only 10 electrons.
- Therefore, because the positive charges in the nucleus are unchanged, there is one excess positive charge on the sodium ion.
- Similarly, chloride ion has one negative charge in excess of the positive charges.
- A sodium ion is positively charged because of the one excess positive charge.
- Similarly chloride ion is negatively charged because of the one excess negative charge. These ions have opposite charges.
- Because of the attraction of the oppositely charged Na+ and Cl– ions they attract and form a bond called ionic or electrovalent bond.
- This type of combination is called ionic bonding.
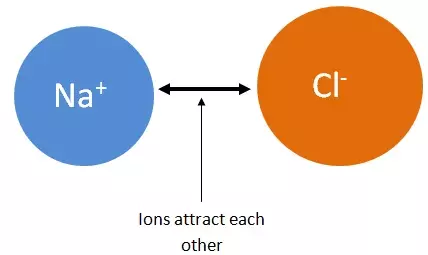
Figure 2: Sodium ion combine with chloride ion
Structure of Sodium Chloride
- The structure of sodium chloride contains numerous sodium and chloride ions in equal proportions.- The electrical attraction electrostatic attraction resulting from their opposite charges constitutes the ionic bond.
- The ions arrange themselves into a rigid solid shape called a crystal.
- Each sodium ion is surrounded by six (6) equidistant chloride ions and vice versa.
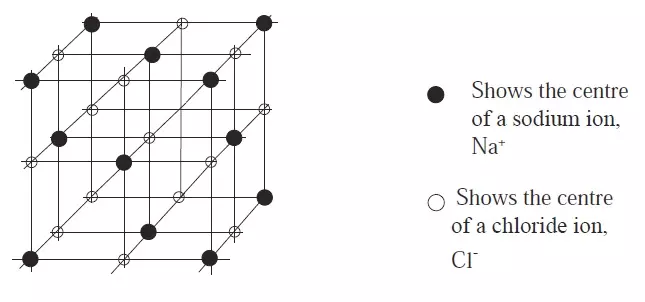
Figure 3: Arrangement of sodium and chloride ions in sodium chloride crystal
- In an end face of the cube a Na+ ion occupies the centre, with six Cl– ions, spaced equally between them.
- The ions form a giant ionic structure.
- The attraction forces between the ions are strong and therefore the ions are not free to move but they vibrate within a given space.
- Consequently the melting point of sodium chloride is high. In solid form, it is a non-conductor of electricity.
- when sodium chloride is melted sodium ions and chloride ions separate and thus their forces of attraction are greatly reduced.
- When an electric current is applied the ions in molten sodium chloride are free to move thereby conducting electricity.
- The positive ions formed as a result of loss of one or more electrons are called cations, and their positive charges are equal to the number of electrons lost.
- Likewise, the negative ions formed as a result of gain of one or more electrons are called anions and their negative charges are equal to the number of electrons gained.
- The number of electrons lost from, or added to, the outermost energy level of the atom of an element during ionic bonding is equal to the combining power (valency) of that element.
- Only the outermost energy level electrons are involved in ionic bonding.
- The number of ions involved must balance the valency requirements of elements as shown in the following examples.
(i) Sodium sulphide
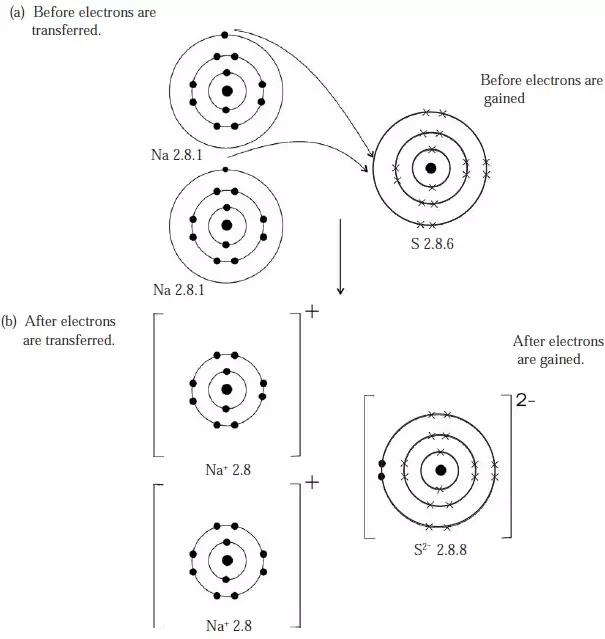
Figure 4: Ionic bond in sodium sulphide (Na2S)
- Therefore the formula of sodium sulphide is Na2S.
- The valency electrons (outermost energy level electrons) from the two sodium atoms are transferred to the outermost energy level of sulphur as shown in Figure 4 above.
(ii) Magnesium oxide
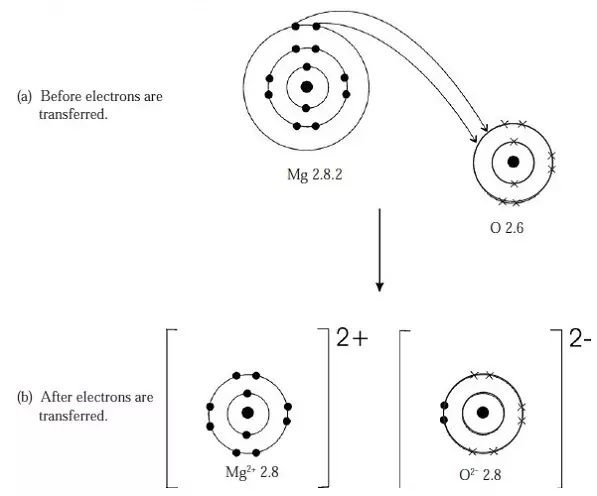
Figure 5: Ionic bond in magnesium oxide (MgO)
- The two valency electrons from one magnesium atom are transferred to one oxygen atom.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
-
1. Ionic compounds are electrolytes (solutions that conduct electric current) when they are in solution or molten form.
2. They have high melting points non-volatile.
3. They are generally soluble in water.
4. Ionic compounds are insoluble in organic liquids like benzene or propanone.
5. They are usually crystalline solids.