Question 1
Use the table below to answer the questions that follow.
(The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements )

(a) Write the electronic arrangement for the ions formed by the elements B and D
(b) Select an element which is
(i) a poor conductor of electricity
(ii) most reactive metal
(c ) Explain briefly how the atomic radii of element B and C compare
(d) Use dots (•) and crosses (x) to represent outermost electrons and show the bonding in the compound formed between C and D.
(e) Explain why the melting point of element B is higher than that of element A.
(f) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place between element A and water
(g) Describe how a solid mixture of the sulphate of element E and lead (II) sulphate can be separated into solid samples
Answer
(a) B – 2 : 8
D – 2 : 8 : 8
(b) (i) D
(ii) E
(c ) Atomic radius of B is larger than that of C. C has more protons. The outer energy level electrons are pulled strongly to the nucleus reducing the atomic size.
(d)

(e) Element B has stronger metallic bond ( has more delocalized electrons ) than A, hence higher amount of heat energy is needed to break the bond.
(f) 2A(s) + 2H2O (l) → 2AOH (aq) + H 2(g)
(g) Add water to the mixture and stir. Filter to obtain lead (II) sulphate as residue and sulphate of E as filtrate Dry the residue to obtain lead (II) sulphate. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness to obtain the solid sulphate of E.
D – 2 : 8 : 8
(b) (i) D
(ii) E
(c ) Atomic radius of B is larger than that of C. C has more protons. The outer energy level electrons are pulled strongly to the nucleus reducing the atomic size.
(d)

(e) Element B has stronger metallic bond ( has more delocalized electrons ) than A, hence higher amount of heat energy is needed to break the bond.
(f) 2A(s) + 2H2O (l) → 2AOH (aq) + H 2(g)
(g) Add water to the mixture and stir. Filter to obtain lead (II) sulphate as residue and sulphate of E as filtrate Dry the residue to obtain lead (II) sulphate. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness to obtain the solid sulphate of E.
Question 2
(a) (i) State Hess’s law.
(ii) Use the thermochemical equations given below to calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethane.

(b) The table below gives the volumes of oxygen gas produced at different times when hydrogen peroxide solution decomposed in the presence of a catalyst

(i) Name the catalyst used for this reaction
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
(iii) On the grid provided, draw the graph of the volume of oxygen gas ( vertical axis ) against time (horizontal axis).
(iv) Using the graph, determine the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide 24th second and 34th second
(v) Give a reason why the total volume of oxygen gas produced after 50 seconds remain constant
Answer
(a) (i) The energy change in converting reactants to products is the same regardless of the route by which chemical change occur.
(ii)

OR
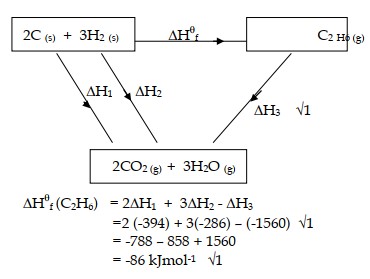
(b)
(i) Manganese (IV) oxide
(ii) 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
(iii)

(iv)

(v) The reactant have been used up
(ii)

OR

(b)
(i) Manganese (IV) oxide
(ii) 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
(iii)

(iv)

(v) The reactant have been used up
Question 3
(a) The diagram below is a set-up to prepare ethyne gas.

(i) Name solid B
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction taking place between solid B and water.
(iii) State the property that makes the gas to be collected by the method shown in the diagram
(iv) State the main commercial use of ethyne.
(b) The scheme below represents some reactions of ethyne. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

(i) Name compound P and draw it’s structural formula
(ii) Name the reagents used in
I) Process R
II) Step I
(iii) Draw the repeating unit in polymer T.
(iv) Name polymer T
(v) Give one use of T
(c ) Ethanol and ethanoic acid react according to the following equation under condition M and process N to form product Z.

Name:
(i) Condition M
(ii) Product Z
(iii) Draw the structural formula of product Z
(iv) State any 1 difference between the above reaction and that of an hydroxide and an acid
(v) Butane is often used as the main component in domestic gas fuels. Calculate it’s heating value

Answer
(a)
(i) Calcium (II) carbide
(ii) CaC2 (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2(aq) + C2H2(g)
(iii) Ethyne gas is insoluble in water
(iv) A mixture of oxygen and ethyne gas forms oxyacetylene flame used for welding and cutting of metals
b)
(i) 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane

(ii) I) Hydrogen gas
II) Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
(iii)

(iv) Polychloroethane
(v) - Making crates and boxes
- Making plastic ropes
(c )
(i) Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
(ii) Ethylethanoate
(iii)

(iv)

(v)

(i) Calcium (II) carbide
(ii) CaC2 (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2(aq) + C2H2(g)
(iii) Ethyne gas is insoluble in water
(iv) A mixture of oxygen and ethyne gas forms oxyacetylene flame used for welding and cutting of metals
b)
(i) 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane

(ii) I) Hydrogen gas
II) Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
(iii)

(iv) Polychloroethane
(v) - Making crates and boxes
- Making plastic ropes
(c )
(i) Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
(ii) Ethylethanoate
(iii)

(iv)

(v)

Question 4
The flow chart below shows the extraction of zinc. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

a) (i) Identify substance X
(ii) Give one waste material of the froth flotation process
(iii) Identify substances A and B
(iv) Write equation for the reaction taking place in the roaster.
(v) Identify gas P and write an equation for it’s formation
b) Use the standard electrode potentials given below to answer the questions that follow

(i) Construct an electrochemical cell that will produce the lowest emf
(ii) Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in (i) above.
(iii) From the half reactions listed in the table in (b) above select strongest oxidizing agent.
Answer
(a)
(i) Frothing agent / vegetable oil
(ii) Sand / clay or galena (PbS) or slurry
(iii) A – Air
B – Sulphur (IV) oxide
(iv) 2ZnS (s) + 3O2(g) → 2ZnO(s) + 2SO2(g) (v) Carbon (II) oxide
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
b)(i)

(ii)
Emf of cell = 0 - 0.13 – ( -0.76)
= -0.13 + 0.76
= + 0.63V
(iii) Ag+ (aq)
(i) Frothing agent / vegetable oil
(ii) Sand / clay or galena (PbS) or slurry
(iii) A – Air
B – Sulphur (IV) oxide
(iv) 2ZnS (s) + 3O2(g) → 2ZnO(s) + 2SO2(g) (v) Carbon (II) oxide
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
b)(i)

(ii)
Emf of cell = 0 - 0.13 – ( -0.76)
= -0.13 + 0.76
= + 0.63V
(iii) Ag+ (aq)
Question 5
(a) Fractional distillation of liquid air is mainly used to obtain nitrogen and oxygen.
(i) Name one substance that is used to remove carbon (IV) oxide from the air before it is changed into liquid.
(ii) Describe how nitrogen gas is obtained from the liquid air. (Boiling points nitrogen = -1960C, Oxygen = -1830C )
(b) Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.

(i) Name substance M
(ii) Identify gas Q
(iii) State one use of compound Z
(iv) A fertilizer manufacturing industry uses 1400dm3 of ammonia gas per hour to produce ammonium sulphate. Calculate the amount of ammonium sulphate produced in kg for one day if the factory operates for 18 hours. ( N = 14, H = 1, S = 32, O = 16, 1 mole of gas = 24dm3 )
Answer
(a)
(i) Potassium hydroxide solution (KOH) or sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH)
(ii) - Heat / boil the liquid air // warm / raise the temperature of liquid air.
- Nitrogen comes out first because it has a lower boiling point than oxygen
(b)
(i) Hydrogen (H2)
(ii) Nitrogen (II) oxide
(iii) Fertilizer
(iv)

(i) Potassium hydroxide solution (KOH) or sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH)
(ii) - Heat / boil the liquid air // warm / raise the temperature of liquid air.
- Nitrogen comes out first because it has a lower boiling point than oxygen
(b)
(i) Hydrogen (H2)
(ii) Nitrogen (II) oxide
(iii) Fertilizer
(iv)

