Question 1
The table below shows some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the question that follow. (The letter are not the actual symbols of the elements)

- Identify the elements in the same group.
- Give the name of the family to which elements P and S belong
- Write the electron configuration of ions of elements;
i. V
ii. Q - Given that isotopes of element S are as follows 39S(93.1%), xS(0.01%) and 41S(6.89%), calculate x given that the relative atomic mass of element S is 39.1349.
- Elements Q and V react to form a compound
i. Write an equation for the reaction
ii. What is the nature of the compound formed in (i) above. Explain
Answer
- P & S
U and R - Alkali metals
-
i. V - 2.8.8
ii. Q3+ 2.8 -

- Elements Q and V react to form a compound
i. 2Q(s) + 3V2(g) → 2QV3
ii.Acidic; QV3/AlCl3 hydrolyses in water to form H+ions, hence the acidic nature of the chloride
Question 2
i. The following set up was carried out by students in form two in the open air in the presence of sunlight to investigate a certain property of the halogen. Study it answer the questions.

a) Which property of the halogen was being investigated
b) Name the gas which was colourless.
c) Chlorine water is yellow in colour. However, in the presence of light it is decolourised. Explain
d) Comment on the effect of chlorine water on red and blue litmus paper
ii. The following diagram represents a section of the plant for the large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid

a) Name gases A and B.
b) State the role of glass beads in the plant
c) Explain why gas A is introduced into the reaction chamber through a jet
d) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between gas A and B.
e) Determine the volume of hydrochloric acid gas formed when 3600cm3 of gas B react with gas A at stp (MGV at stp = 22.4dm3)
f) CFC’S and DDT are chlorine compounds with long life span and so affects both plants and animal life. Write their full names.
CFC
DDT
Answer
i.
a) Solubility in water.
b) Oxygen
c) The yellow colour is due to presence of chloric (I) acid; in the presence of light the chloric (I) acid decompose to form hydrochloric acid, hence the solution turn colourless
d) Blue litmus paper turns red then both litmus papers are bleached to white; chlorine water is acidic and has bleaching properties due to presence of chloric (I) acid/ hypochlorous acid.
ii
a) A – Hydrogen
B – Chlorine
b) To increase the surface area over which the gas dissolves in water.
c) To prevent an explosion since the mixture of chlorine and hydrogen react explosively.
d) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
e)

f) CFC – chlorofluorocarbons
DDT – Dichlorodiphenytrichloroethane
a) Solubility in water.
b) Oxygen
c) The yellow colour is due to presence of chloric (I) acid; in the presence of light the chloric (I) acid decompose to form hydrochloric acid, hence the solution turn colourless
d) Blue litmus paper turns red then both litmus papers are bleached to white; chlorine water is acidic and has bleaching properties due to presence of chloric (I) acid/ hypochlorous acid.
ii
a) A – Hydrogen
B – Chlorine
b) To increase the surface area over which the gas dissolves in water.
c) To prevent an explosion since the mixture of chlorine and hydrogen react explosively.
d) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
e)

f) CFC – chlorofluorocarbons
DDT – Dichlorodiphenytrichloroethane
Question 3
i. Butane and bromine react according to the equation below
CH3CH2CH2CH3 + Br2 → CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + HBr
a) Name the type of reaction taking place in the equation above
b) State the condition under which the above reaction takes place. Explain
c) Name the following compounds
i

ii

iii

ii. Study the reaction scheme shown and answer the questions that follow.

a) Identify reagent A
b) Name process;
i. X
ii. W
c) Write the equation for the process J
d) Name products
S
T
V
e) Draw and name the structure of:
i. Polymer Z
ii. Product U
Answer
i.
a) Substitution
b) U.V light/ sunlight; presence of sunlight splits the halogen (bromine) molecules into free atoms which are very reactive hence they replace the hydrogen atoms in an alkane.
c) i. Name 2,3 - dimethylpentane
ii. Name 1,3 – dichloro – 2 - methylbutane
iii. Name: 5 – methylhex-1-ene
ii.
a) Hydrogen
b) i. X - Hydrolysis
ii. W - Halogenation
c)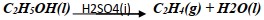
d) S – Bromoethane
T – 1, 2 - dibromoethane
V – Ethanol
e)
i.
ii.
b) U.V light/ sunlight; presence of sunlight splits the halogen (bromine) molecules into free atoms which are very reactive hence they replace the hydrogen atoms in an alkane.
c) i. Name 2,3 - dimethylpentane
ii. Name 1,3 – dichloro – 2 - methylbutane
iii. Name: 5 – methylhex-1-ene
ii.
a) Hydrogen
b) i. X - Hydrolysis
ii. W - Halogenation
c)
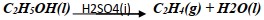
d) S – Bromoethane
T – 1, 2 - dibromoethane
V – Ethanol
e)
i.

ii.

Question 4
Use the flow chart drawn to answer the questions that follow:

a) Identify:
i. Compound C
ii. Compound K
b) Write the equation for the following
i. Calcium hydroxide and substance C.
ii. Gas W and ammonia
c) Identify the catalyst in step II
d) Write the formula of the deep blue solution and compound K.
e) State the type of reaction that produces P
f) i. State one use of compound K
ii. When compound N is heated, a red-brown gas is evolved and a yellow residue is left on cooling.
g) Name:
i. The red-brown gas.
ii. The ions present in the residue.
iii. Write equation for decomposition of solid N.
Answer
a)
i. Compound C - Ammonia chloride
ii. Compound K - Ammonium nitrate
b)
i. Ca(OH)2(s) + 2NH4Cl(s) → CaCl2(aq)+ 2NH3(g)+2H2O(l)
ii. NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
c) Platinum rhodium
d) i. [Cu(NH3)4 ]2+
ii. NH4NO3
e) Neutralization
f) i. As a fertilizer
ii. NH3(g) + HCl(g) NH4Cl(s)
g)
i. Nitrogen (IV) oxide.
ii. Pb2+ and NO-3 ions
iii. 2Pb(NO3)2(s) heat → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g)+ O2(g)
i. Compound C - Ammonia chloride
ii. Compound K - Ammonium nitrate
b)
i. Ca(OH)2(s) + 2NH4Cl(s) → CaCl2(aq)+ 2NH3(g)+2H2O(l)
ii. NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
c) Platinum rhodium
d) i. [Cu(NH3)4 ]2+
ii. NH4NO3
e) Neutralization
f) i. As a fertilizer
ii. NH3(g) + HCl(g) NH4Cl(s)
g)
i. Nitrogen (IV) oxide.
ii. Pb2+ and NO-3 ions
iii. 2Pb(NO3)2(s) heat → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g)+ O2(g)
Question 5
a) Candle wax is mainly a compound consisting of two elements. Name the two elements
b) The set – up below was used to investigate the burning of a candle. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

i. What would happen to the burning candle if the pump was turned off? Give reasons
ii. State and explain the changes in mass that are likely to occur in tube N by the end of the experiment
iii. Name two gases that come out through tube M
iv. What is the purpose of calcium chloride in tube L
v. Name another substance that could be used in the place of calcium oxide in tube N.
Answer
(a) i. Hydrogen
ii. Carbon
(b) i. It extinguishes because carbon (IV) oxide will accumulate around it putting it off.
ii. Mass increase since water vapour reacts with calcium oxide, Cao, and forms calcium hydroxide, which then reacts with carbon (IV) oxide to produce calcium carbonate
iii. 1. Nitrogen,
2. Helium,
3. ArgonM
iv. It absorbs moisture which is produced from burning candle
v. Sodium hydroxide
ii. Carbon
(b) i. It extinguishes because carbon (IV) oxide will accumulate around it putting it off.
ii. Mass increase since water vapour reacts with calcium oxide, Cao, and forms calcium hydroxide, which then reacts with carbon (IV) oxide to produce calcium carbonate
iii. 1. Nitrogen,
2. Helium,
3. ArgonM
iv. It absorbs moisture which is produced from burning candle
v. Sodium hydroxide
