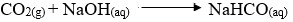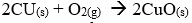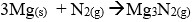Question 1
The diagram below shows the process of manufacturing sodium carbonate using ammonia soda process. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
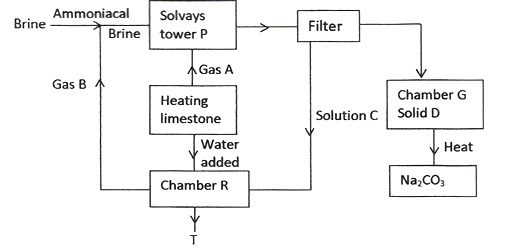
- Name gases A and B
- A
- B
- Name liquid C and solid D
- C
- D
- Write equations of the reactions in:
- Tower P
- Tower R
- Name the product T formed at chamber R and give one of its uses.
Answer
-
- A - Carbon (IV) oxide
- B - Ammonia
-
- C - Ammonium chloride solution
- D - Sodium hydrogen carbonate
-
- Tower P -
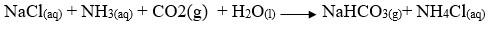
- Tower R -
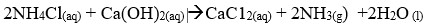
- Tower P -
- Calcium chloride
- Drying agent
- Lower me during extraction of sodium
Question 2
The set-up below was used to prepare and collect gas X. During the experiment cleaned magnesium ribbon was strongly heated before heating the wet glass wool.
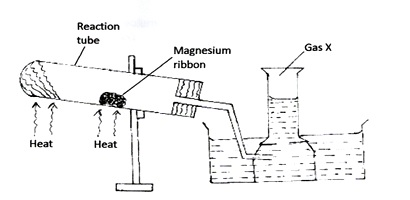
- Name gas X
- Why is magnesium ribbon cleaned before it is used?
- State one observation that would be noted in the reaction tube.
- Write the equation for the reaction in the reaction tube.
- State one industrial use of the solid product formed in the reaction tube.
- What precaution should be taken at the end of experiment? Explain.
- At the end of the experiment 96.0cm3 of gas X were collected at 10°C and 1 atmosphere pressure. (Mg = 24, M.G.V = 22.4, T =0°C at stp, P = 1 atmosphere at sip).
(i) Determine the volume gas X would occupy at s.t.p?
(ii) Calculate the mass of magnesium ribbon used Mg = 24
Answer
- X - Hydrogen gas
- Remove magnesium oxide layer on the surfaces.
- Bright white light or White powder
-
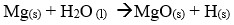
- Brick liners in furnaces.
- Withdraw delivery tube from water before you stop heating to prevent sucking back.
-
(i)
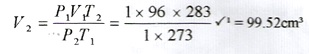
(ii)

Question 3
Air was passed through several reagents as shown in the flow chart below.
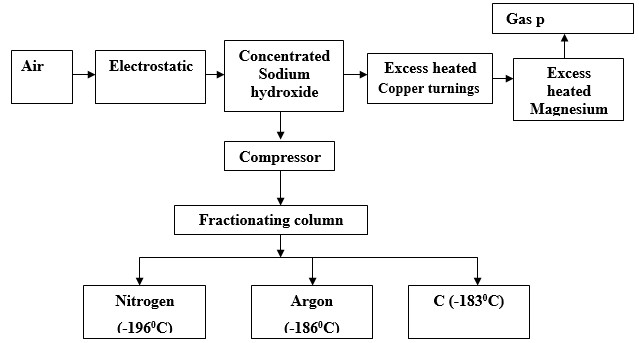
- Name the major components of air.
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the chamber with:
- Concentrated sodium hydroxide
- Excess heated copper turnings
- Excess heated magnesium powder
- Name one gas which escapes from the chamber containing magnesium powder. Give a reason for your answer.
- Name the substance that was eliminated by electrostatic precipitation.
- Name a reagent that can be used in place of concentrated sodium hydroxide.
- Name substance C
- State three uses of gas C.
Answer
- Oxygen and Nitrogen
-
-
- Neon/ Argon / Helium - They are stable and thus unreactive
- Dust
- Concentrated potassium hydroxide
- C - Oxygen
- • Used in deep sea diving.
• Used in hospitals by patients with breathing difficulties.
• Used in high altitude flying
Question 4
Study the information below and answer the questions that follow
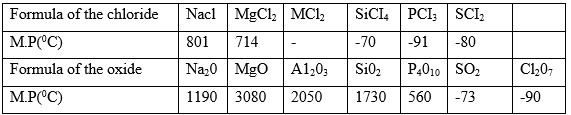
- Aluminium chloride AlCl3 has an unexpected bond type and structure.
- State the type of bond and the structure in AlCl3.
Bond type
Structure - What type of bonding would AlCI3 be expected to have why?
- Why is the melting point of AlCI3 not indicated in the table above?
- State the type of bond and the structure in AlCl3.
- A piece of blue litmus paper is placed in a solution of sodium chloride and a solution of aluminium chloride. Explain what would be observed in each case.
Sodium chloride solution
Aluminium chloride solution - Explain the large difference in the melting point of the compound of formula MgO and P4O10.
- Write down the equations for the reaction between the compounds of formula Na2O and water.
- Silicon(IV) chloride gets hydrolyzed by water Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
Answer
-
-
Bond type - Covalent bond
Structure - Simple molecular - Ionic bond - Because it is a compound of a metal and a non- metal.
- AlCI33 sublimes when heated
-
Bond type - Covalent bond
-
Sodium chloride solution - There is no effect on blue litmus paper because NaCl solution is neutral.
Aluminium chloride solution - Blue litmus paper turned red because the solution is acidic due to hydrolysis of Al3+ AlCl3. - MgO has much higher than P4O10 because MgO has strong ionic bonds with giant ionic structure while P4O10 has simple molecular structure with weak Van der Waals forces.
-
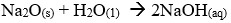
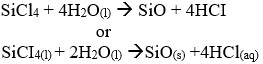
Question 5
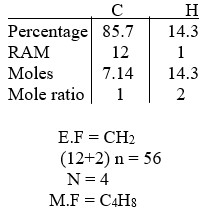
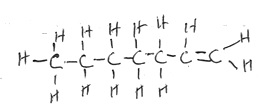
A compound Z has a molar mass of 56g and contains 853% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass.
(C = 12, H = 1)
-
- Determine the molecular formula of compound Z.
- Give the structural formula of the sixth member of the homologous series to which Z belongs.
- Compound Z reacts with a few drops of acidified potassium chromate (VII) solution
- State the observation made during the reaction.
- Name the organic product formed in the reaction on (c) above.
- Z reacted with liquid bromine in the dark (room conditions).
- State the observation made during the reaction
- Write the equation for above.
- Name the organic product formed in (d) above.
- State the type of reaction in (d) above.
Answer
-
-
- Potassium chromate (VI) turns from orange to green
- Butan — 1-ol or Butan — 2-ol
-
- Brown bromine is decolorized
-
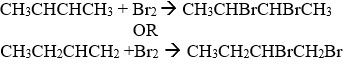
- 2,3 — dibrornobutane or 1,2 — dibromobutane
- Addition