Question 1
Use the grid below to answer the questions that follow. Letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements.

- What family name is given to elements G and H?
- State and explain the difference in reactivity between.
- I and J
- N and P
- How does atomic radius of K compare to that of L? Explain.
- Explain the trend in melting points down the group of elements to which I and J belong.
- Write down an equation for the reaction between K and P.
- Give one use of element Q.
- Write down the electronic arrangement of a stable ion of H.
Answer
- Alkali metals
- State and explain the difference in reactivity between.
- J is more reactive than I because J loses valence electrons more easily since it has more occupied energy levels
- P is more reactive than N because P gains an electron more easily it has a smaller atomic radius than N
- K has a larger atomic radius because it has a weaker nuclear charge attraction than L
- Melting point decreases down the group because metallic bonding weakens as atomic size increases down the group
- 2K(s) + 3P2(g) → 2KP3(s) OR
2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) → 2AlCl3(s) - In light bulbs to prevent oxidation of the filament As an insulator in arch-welding
- 2.8.8
Question 2
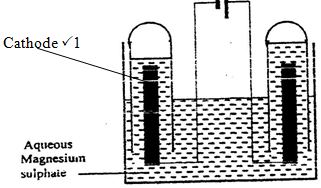
The set-up below was used during the electrolysis of aqueous magnesium sulphate using inert electrodes.

-
- Name a suitable pair of electrodes for this experiment.
- Identify the anions and cations in the solution
- On the diagram label the cathode.
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place at the cathode.
- Explain the change that occurred to the concentration of magnesium sulphate solution during the experiment
- During the electrolysis, a current of 2 amperes was passed through the solution for 4 hours. Calculate the volume of the gas produced at the cathode. (1 Faraday= 96500 coulombs , molar volume of a gas at room temperature = 24000cm3)
- One of the uses of electrolysis is electroplating.
- Give two reasons why electroplating is necessary.

- On the diagram, show with a (+) sign the positive terminal
- Write the equation for the reaction in which electrons are produced
- Give one disadvantage of dry cells.
Answer
-
- Graphite(carbon)
- Anions: SO42- , OH-
Cations: Mg2+, H+ -
- 2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g)
- Concentration increased because the amount of water decreased as it was decomposed to hydrogen and oxygen gases which escaped

- To prevent corrosion
To enhance the beauty of the article

- Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
- Cannot be recharged
Question 3
The scheme below shows the industrial manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

-
- State two functions of the chamber A.
- Explain why concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid is used in the absorption chamber and not water
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place at the absorption chamber
- Name two catalysts that can be used in the catalytic chamber
- Sulphuric (VI) acid is used in making fertilizers. What volume of ammonia gas will be required to make 25kg of ammonium sulphate?( N = 14, H = 1.0, S = 32, O = 16.0 Molar gas volume at r.t.p=24.0dm3)
- The equation below shows the oxidation of Sulphur (IV) oxide to Sulphur (VI) oxide in the contact process.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) ∆H = -196kJ/mol-- State and explain the effect on the yield of Sulphur (IV) oxide when.
- the temperature increased.
- the amount of oxygen is increase
- State and explain the effect on the yield of Sulphur (IV) oxide when.
Answer
-
- Preheating of gases / cooling of gases
- Reaction with water is exothermic, heat generated boils the acid forming tiny misty droplets in air
- SO3(g)+H2SO4(l) → H2S2O7(l)
- Platinum and Vanadium (V) oxide

-
-
- Yield decreases 1 forward reaction is exothermic
- Yield increases 1 Oxygen reacts with Sulphur (IV) oxide forming more Sulphur (VI) oxide
-
Question 4
Study the following table and then use it to answer the questions that follow.

- These organic compounds belong to the same homologous series
- What is meant by the term homologous series?
- Select one hydrocarbon that would be a liquid at room temperature
- Compare the boiling point of CH4 and C6H14 ? Explain your answer
- Give one chemical test to distinguish between C2H6 and C2H4
- What is meant by the term homologous series?
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow

- Name the reagents used in Step I
Step II
- Write an equation for the complete combustion of CH≡CH
- Explain one disadvantage of the continued use of items made from the compound formed in Step III
- Name the reagents used in Step I
Step II
Answer
- Group of compounds with similar chemical properties, chemical formulae and they exhibit a steady gradual change in physical properties
- Alkanes
- C6H14
- C6H14 has a higher boiling point than CH4 it has more carbon atoms thus increased strength of the Van der Waals forces
- Bubble both substances separately into acidified pottasium manganate(VII) or potassium chromate(VI) solution solution turns from purple to colourless in C2H4 and remains purple in C2H6 /turns from orange to green in C2H4 and remains green in C2H4
- Group of compounds with similar chemical properties, chemical formulae and they exhibit a steady gradual change in physical properties
- Step I hydrogen gas
Step II hydrogen chloride
- C2H2(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
- they cause environmental pollution because they are non biodegradable.
- Step I hydrogen gas
Question 5
Study the flow diagram below and answer the questions that follow:-

-
- Describe how nitrogen is obtained from air
- Name the element M
- Write an equation for the reaction in step 7
- State two uses of ammonia gas
- State and explain the observations made if a sample of sulphur is heated in concentrated Nitric(V) Acid
Answer
-
- First pass the air through concentrated potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide which absorbs carbon (iv)oxide
- The remaining part of air is then passed over heated copper turnings to remove oxygen
- The residual gas is then collected
-
- First pass the air through concentrated potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide which absorbs carbon (iv)oxide
- Hydrogen gas
- To ensure all the ammonia gas is oxidized to NO2
- - as a fertilizer
- removal of greasy stains
