Question 1
The grid below is part of the periodic table. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements). Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
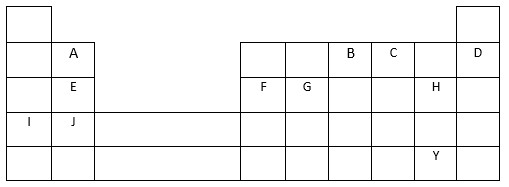
- State the chemical family to which the following elements J and D belong.
- J
- D
-
- Write the formula of the compound formed when J reacts with B.
- Write an equation for the reaction between the compound formed in (i) and water.
- How does the reactivity of E compared with that of F? Explain
- On the grid show by using letter L the first longest period and give a reason why you think it is the first longest period.
- Write the formula of the ion of F and give the equation of its formation.
- Ion
- Equation
Answer
-
- J - Alkaline earth metals
- D - Noble gas elements
-
- J3B2
-

- E is more reactive than F, across the period there is an increase nuclear charge due to increase in the number of protons, thus E has a weaker nuclear charge than H and can easy lose its valence electron than H OR This is because of the increase in nuclear charge from E atom to F atom, which makes it easier to remove an electron from E atom to F atom.
- (Period 4)
Reason: It consists of 10 more transition metal elements -
- Ion - Fe3+
- Equation -

Question 2
- You are provided with the following reagents; dilute nitric acid, dilute sulphuric acid, and lead (II) oxide. Describe how you would prepare a sample of lead (II) sulphate.
- Given a mixture of lead (II) chloride, iodine, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride crystals. Describe how you would separate all he four solids using methyl benzene, a source of heat and water.
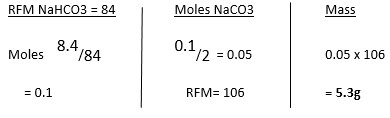
(Hint; Step one involves addition of methyl benzene) - 8.4g of sodium hydrogen carbonate is completely decomposed by heat. Calculate
i) Mass of residue produced
ii) Volume of carbon (IV) oxide produced at s.t.p
(H =1, C = 12, O = 16, Na = 23, Molar gas volume = 22.4dm3)
Answer
- - Add lead (II) oxide till in excess
- Filter to obtain lead (II) nitrate as filtrate
- Mix filtrate with sulphuric acid
- Filter to obtain lead (II) sulphate precipitate - - Add methyl benzene, iodine dissolves
- Filter and crystallisefilterateto obtain iodine
- Heat residue Ammonium chloride sublimes
- Add water to residue, sodium chloride dissolves
- Filter and crystallisefilterate -
i)

ii)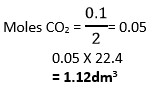
Question 3
Study the reaction scheme below and answer the questions that follow
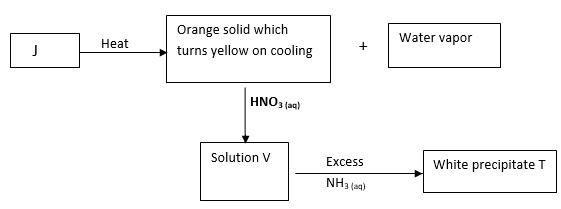
- Identify
i) Solution V
ii) White precipitate T - Write an equation for the reaction forming solution V
- Write an ionic equation to show how the white precipitate T is formed.
Answer
-
i) Solution V - Pb(NO3)2
ii) White precipitate T - Pb(OH)2 -

-

Question 4
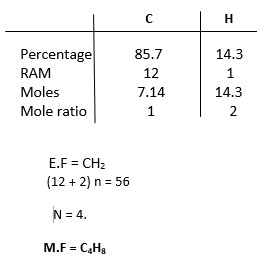
A compound Z has a molar mass of 56g and contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass.
(C = 12, H = 1)
- i) Determine the molecular formula of compound Z.
ii) Give the structural formula of the sixth member of the homologous series to which Z belongs. - Draw and name 2 isomers of Z.
- Compound Z reacts with a few drops of acidified potassium chromate (VII) solution.
i) State the observation made during the reaction.
ii) Name the organic product formed in the reaction on (c) above. - Z reacted with liquid bromine in the dark (room conditions)
i) State the observation made during the reaction
ii) Write the equation for the reaction in (d) above.
iii) Name the organic product formed in (d) above.
iv) State the type of reaction in (d) above.
Answer
- i)
ii)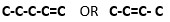
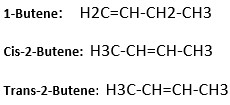
-
i) Potassium chromate (VI) turns from orange to green
ii) Butan– 1-ol or Butan–2-ol -
i) Brown bromine is decolorized.
ii)
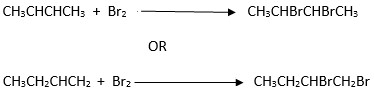
iii) 2,3–dibromobutane or 1,2 – dibromobutane
iv) Addition
Question 5
Study the schematic diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow
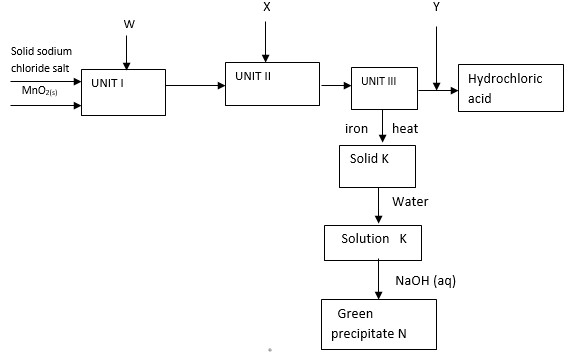
- Identify substances
- W
- X
- Y
- Write an equation for the reaction between solid sodium chloride and substance W.
- State the role of manganese (IV) oxide, MnO2, and substance W.
- Write chemical equations for the reaction;
- Forming solid K
- Producing green precipitate N
Answer
-
- W - Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- X - Hydrogen
- Y - Water
-

- MnO2(s) oxidizes HCl (g) to chlorine
W reacts with NaCl(s) to form HCl(g) -
-


