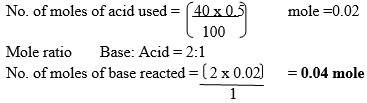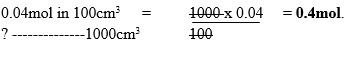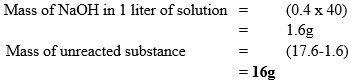Question 1
The flow chart below represents preparation and properties of oxygen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
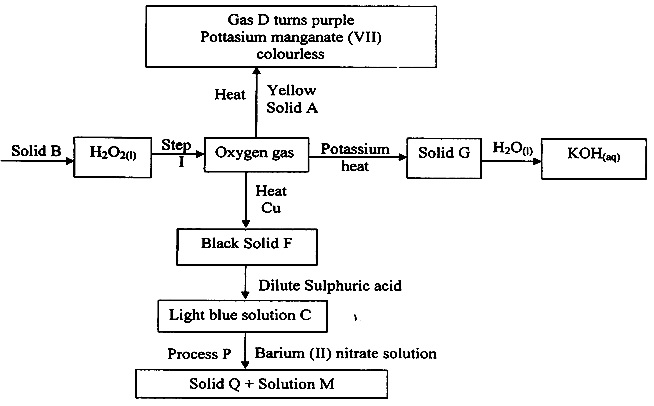
One of the components in the mixture T was sodium chloride.
- Identify the following substances
- Solid A
- Gas D.
- Solid Q
- Solution M
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction in step I.
- Write chemical equation for the formation of the following compound
- Solid G
- Gas D.
- Light blue solution C.
- State the confirmatory test for oxygen gas.
- Write the ionic equation for reaction taking place in process P.
Answer
-
- Solid A - Sulphur
- Gas D - Sulphur (IV) Oxide (SO2(g))
- Solid Q - Barium sulphate (BaSO4(s))
- Solution M - Copper (II) Nitrate (CO(NO3)2(aq))
- 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
-
- Solid G - 4K(s) + O2 → 2K2O(s)
- Gas D - S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
- solution C - Cu(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) + H2O(l)
- Relights a glowing splint.
- Ba2+(aq) + SO2-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
Question 2
State one use of oxygen.
Answer
- Oxy-acetylene flame used in welding.
- Oxygen enriched air is used in hospitals by patients with breathing difficulties.
- When mixed with heliumit is used by mountain climbers and deep-sea divers.
- Remove iron impurities during steel making.
Question 3
The following table gives information on four elements by letters W, X, Y and Z.
Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
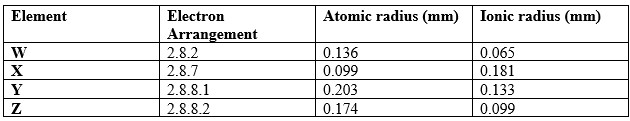
- Which two elements have similar properties? Explain.
- What is the most likely formula of the oxide of X.
- Which element is a non-metal? Explain.
- Explain the difference in the atomic radii of Y and Z.
Answer
- W and Z - Belongs to the same chemical family.
- X2O7
- X - Its ionic radius is larger than its atomic radius or has 1 electron in the outermost energy that can easily be lost.
- Atomic radius of Z is smaller than that of Y because Z has a greater nuclear charge(more protons) that tends to pull its outer electrons more strongly inwardly reducing the size of the atom.
Question 4
Sodium hydroxide pellets were accidentally mixed with sodium chloride. 17.6g of the mixture were dissolved in water to make one litre of solution. 100cm3 of the solution was neutralized by 40cm3 of 0.5M sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place.
- Calculate:
- Number of moles of the substance that reacted with sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Number of moles of the substance that would react with sulphuric (VI) acid in one liter of solution.
- Mass of the unreacted substance in one litre of solution.
(H=1, Na=23, Cl=35.5, O=16).
Answer
Question 5
Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
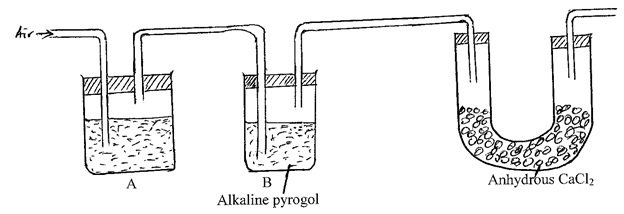
- Solution in reagent Bottle A is used to absorb CO2 gas, name it and write the equation for the reaction of excess CO2 and the solution.
- Name the component removed in reagent bottle B.
- Name 2 impurities of nitrogen collected through this method.
Answer
- Sodium hydroxide/potassium hydroxide.
- Oxygen
- Argon and Neon