- It is one of the fundamental characteristics of living things.
Read More On
- Introduction to Nutrition in Plants and Animals
- Photosynthesis - Dark and Light Reaction stages
- Chemicals of Life
- Heterotrophism and Dentition
- Digestion
- Absorption
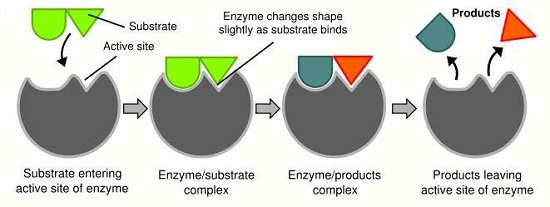
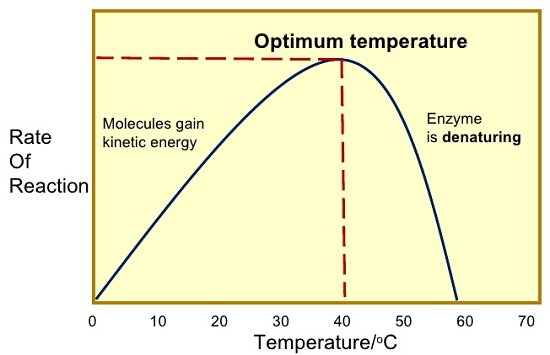
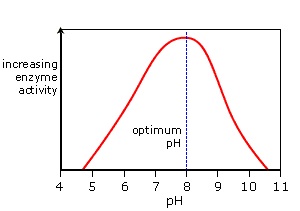
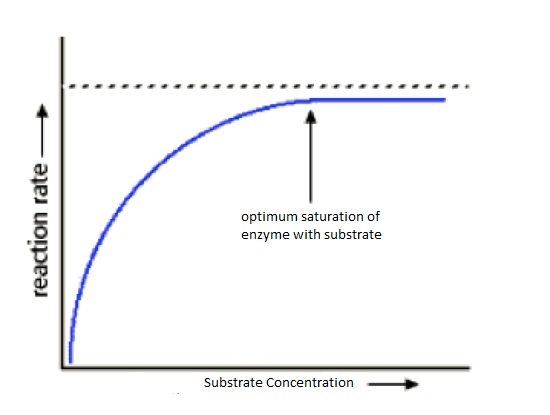
Competitive Inhibitors
- These are chemical substances which are structural analogs of the substrates i.e. they take up the shape of the substrates and compete for the active sites of the enzymes.
- They bind with the enzymes and do not disentangle easily (they stay in the enzyme active site for a long time) thereby slowing down the rate of enzyme activity.
- The reaction can be increased by increasing the substrate concentration.
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
- These are inhibitors that do not resemble the substrate molecules but they combine with the enzyme at any site other the active site and alter the structure of the active site of the enzyme.
- The normal substrate, therefore, fails to bind to the active site leading to decreased rate of reaction.
- Note that these substances do not compete for the active sites of the enzymes.
- The enzymes are destroyed permanently hence the effect cannot be reversed.
- Heavy metals (such as lead, mercury, silver), Cyanide, organophosphates such as malathion are all Non-Competitive Inhibitors