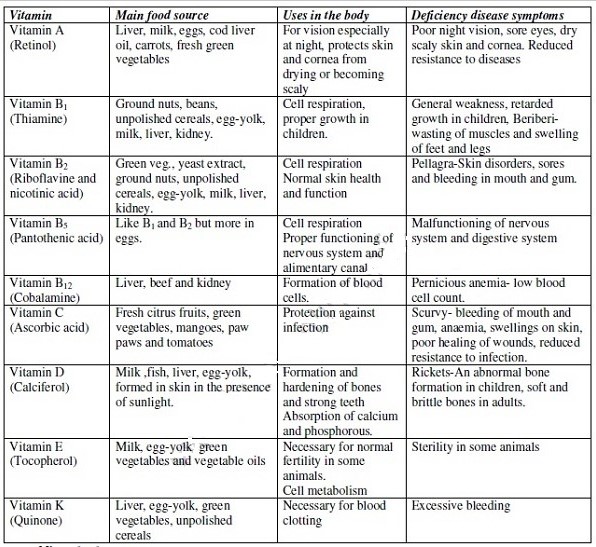
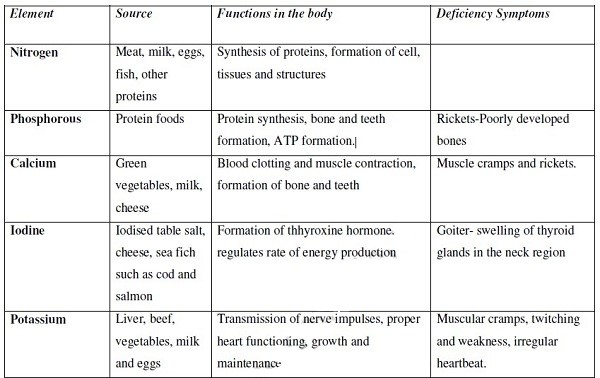
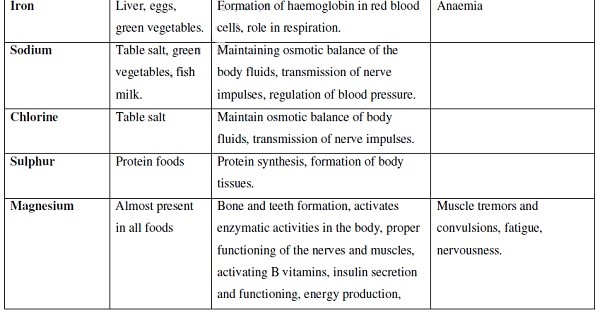
- It is one of the fundamental characteristics of living things.
Read More On
- Introduction to Nutrition in Plants and Animals
- Photosynthesis - Dark and Light Reaction stages
- Chemicals of Life
- Enzymes
- Heterotrophism and Dentition
- Digestion
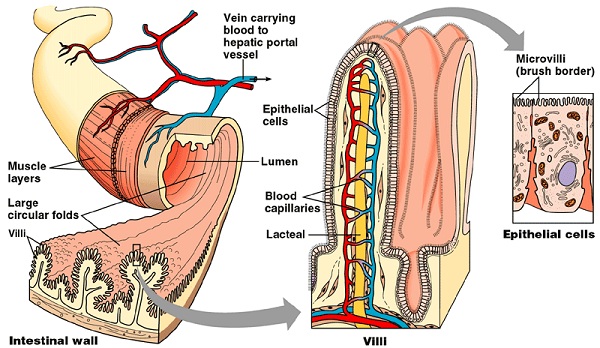
a) Glucose
- Oxidized to release energy
- Excess glucose is stored under the skin to provide heat insulation
- Glucose is used to synthesize complex polysaccharide such as cellulose that is an important structural compound in plants.
b) Fatty acids and glycerol
- Oxidized to release energy
- Combine to form neutral fats stored under the skin to provide heat insulation
- Used to build structures
c) Amino acids
- Used to synthesize proteins for general body growth
- Oxidized during starvation to release energy.