Last Updated: 01-01-2022 | Esoma-KE
Definition of Excretion
- Excretion is the process by which living organisms separate and eliminate waste products of metabolism from body cells.- If these substances were left to accumulate, they would be toxic to the cells.
- Egestion is the removal of undigested materials from the alimentary canals of animals.
- Secretion is the production and release of certain useful substances such as hormones, sebum and mucus produced by glandular cells.
- Homeostasis is a self-adjusting mechanism to maintain a steady state in the internal environment.
Excretion in Plants
- Plants have little accumulation of toxic waste especially nitrogenous wastes.- This is because they synthesise proteins according to their requirements.
- In carbohydrate metabolism plants use carbon (IV) oxide released from respiration in photosynthesis while oxygen released from photosynthesis is used in respiration.
- Gases are removed from the plant by diffusion through stomata and lenticels.
- Certain organic products are stored in plant organs such as leaves, flowers, fruits and bark and are removed when these organs are shed.
- The products include tannins, resins, latex and oxalic acid crystals.
- Some of these substances are used illegally.
- Khat, cocaine and cannabis are used without a doctor's prescription and can be addictive.
- Use of these substances should be avoided.
Excretory Products in Plants: Source and Uses
| Plant | Source | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | Tea and coffee | Mild CNS stimulant. |
| Quinine | Cinchona tree | Anti malaria-drug |
| Tannins | Barks of Acacia, Wattle trees | Tanning hides and skins |
| Colchicine | Corms of crocus | Prevents spindle formation in cell division |
| Cocaine | Leaves of coca plant | Local anaesthesia |
| Rubber | Latex of rubber plant | Used in shoe industry |
| Gum | Exudate from acacia | Used in food processing and printing industry |
| Cannabis | Flowers, fruits and leaves of cannabis sativa | Used in manufacture of drugs |
| Nicotine | Leaves of tobacco plant | Manufacture of insecticides. Heart and CNS stimulant |
| Papain | Pawpaw (fruits) | Meat tenderiser Treats indigestion |
| Khat | Khatha edulis (miraa) | Mild stimulant |
| Morphine | Opium Poppy plant | Narcotic. Induces sleep / hallucinations |
| Strychnine | Seeds of strychnos | CNS stimulant |
Excretion in Animals
Excretory Products in Animals
| Substance | Origin |
|---|---|
| 1. Nitrogenous compounds: (i) Ammonia (ii) Urea (iii) Uric acid |
Excess amino acids (proteins). Deamination of amino acids. Deamination of amino acids; then addition of carbon dioxide. Ammonia (from deamination of amino acids). |
| 2. Carbon dioxide | Homeostasis (any self-regulating process by which an organism tends to maintain stability while adjusting to conditions that are best for its survival) and respiration (process by which energy is liberated from organic compounds such as glucose) |
| 3. Biliverdin (Latin for green bile) and bilirubin (a yellowish pigment that is made during the normal breakdown of red blood cells) | Breakdown of haemoglobin. |
| 4. Water | Osmoregulation (refers to the physiological processes that maintain a fixed concentration of cell membrane-impermeable molecules and ions in the fluid that surrounds cells) |
| 5. Cholesterol | Excess intake of fats |
| 6. Hormones | Excess production |
Excretion and Homeostasis in Unicellular Organisms
- Protozoa such as amoeba depend on diffusion as a means of excretion.- They have a large surface area to volume ratio for efficient diffusion.
- Nitrogenous waste and carbon (IV) oxide are highly concentrated in the organism hence they diffuse out.
- In amoeba excess water and chemicals accumulation in the contractile vacuole.
- When it reaches maximum size the contractile vacuole moves to the cell membrane, bursts open releasing its contents to the surroundings.
Excretion in Human Beings
- Excretion in humans is carried out by an elaborate system of specialised organs.- Their bodies are complex, so simple diffusion cannot suffice.
- Excretory products include nitrogenous wastes which originate from deamination of excess amino acids.
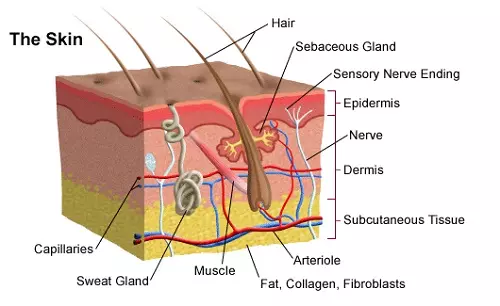
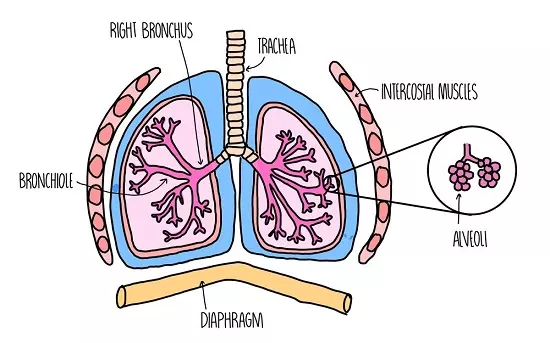
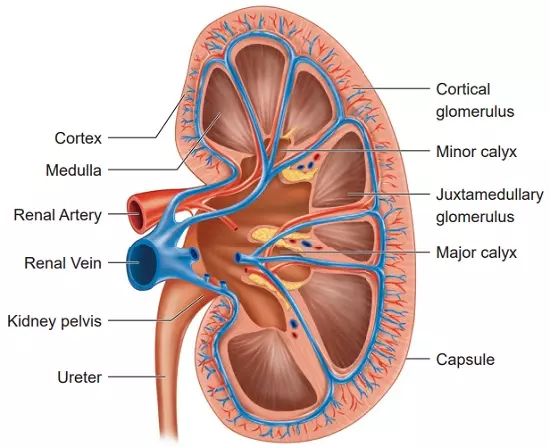
- The main excretory organs in mammals such as human beings include lungs, kidneys, skin and liver.