Question 1
1. The diagram below represents a plant tissue
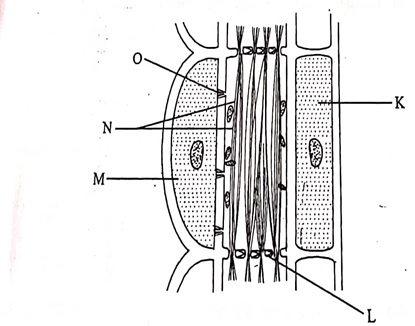
a) Name the structures L and O
L
O
b) State the function of structure N and cell labelled M
N
M
c) Give two structural differences between phloem tissue and xylem tissue.
d) Distinguish between active and passive immunity.
Answer
a)
L - Sieve plate
O - Plasmodemata
b) N - Allows for continous movement of manufactured good substances along them
M - Provide energy for translocation.
c)
d) Passive immunity is atype of immunity that results from transfer of antibodies from one animal to the other while Active immunity is a type of immunity where the animals's body produces its' own antibodies.
O - Plasmodemata
b) N - Allows for continous movement of manufactured good substances along them
M - Provide energy for translocation.
c)
| Phloem | Xylem |
|---|---|
| - Made of living cells | - Made of dead cells |
| - Has cross walls that form sieve plates | - Lack cross walls |
d) Passive immunity is atype of immunity that results from transfer of antibodies from one animal to the other while Active immunity is a type of immunity where the animals's body produces its' own antibodies.
Question 2
The following figures represent the forelimb of a certain animal species. Study them and answer the questions that follow
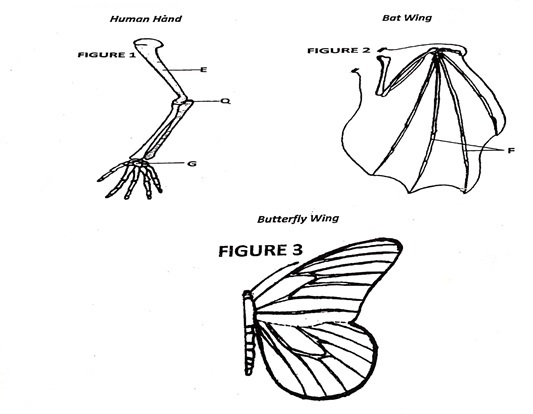
a) Name the bones labelled E and G
E
G
b) State the type of skeleton represented by figure 1.
c) Name the type of joint at point Q.
d) Which two figures represent analogous structures?
e) Give adaptational differences between structures in figure 1 and 3.
Answer
a)
E - Humerus
G - Carpal
b) Endoskeleton
c) Hinge
d) Figure 2 and 3
e) Human hand has five digits separated into four fingers and an opposable thumb for grabing or manipulation while bat wing has five digits which are long and spread out to support a large membranous wing for flight.
G - Carpal
b) Endoskeleton
c) Hinge
d) Figure 2 and 3
e) Human hand has five digits separated into four fingers and an opposable thumb for grabing or manipulation while bat wing has five digits which are long and spread out to support a large membranous wing for flight.
Question 3
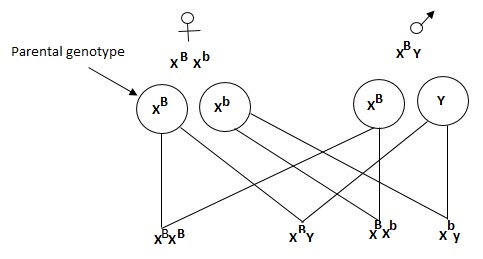
3. Colour blindness is a disorder caused by gene mutation and it is controlled by a recessive gene. A man with normal colour vision marries a carrier woman.
a) Using letter B to represent the gene for normal color vision, what is the chance that their son will be colour blind? Show your working.
b) Name another trait in humans inherited in the same way as color blindness
c) Briefly describe inversion in gene mutation
d) Distinguish between back cross and testcross
Answer
a)
b) Haemophilia
c) Portion of DNA stored breaks at two points, rotates through 180o and then rejoins in an inverted manner.
d) Back cross is a cross between an off spring with unknown parental genotype while Test cross is a cross between an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual.

b) Haemophilia
c) Portion of DNA stored breaks at two points, rotates through 180o and then rejoins in an inverted manner.
d) Back cross is a cross between an off spring with unknown parental genotype while Test cross is a cross between an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual.
Question 4
a) Nitrogen in the atmosphere cannot be directly utilized by plants. State two ways by which this nitrogen is made available for plant use
b) State the importance of saprophytic bacteria in the environment.
c) Briefly explain the how excessive use of fertilizers affects the large water bodies.
d) Explain how competition regulates the animal population in a habitat.
Answer
a) 1. Fixation by lightning.
2. Fixation by micro-organisms eg nitrogen fixing bacteria / algae
b) Decomposition of dead organic matter releasing nutrients in the soil.
c) Causes rapid growth of phytoplanktons / small water plants leading to low light intensity in water hence decreasing primary productivity.
d) Organisms with advantagious variations survive and continue with the generation while those with disadvantagious various migrate or die.
2. Fixation by micro-organisms eg nitrogen fixing bacteria / algae
b) Decomposition of dead organic matter releasing nutrients in the soil.
c) Causes rapid growth of phytoplanktons / small water plants leading to low light intensity in water hence decreasing primary productivity.
d) Organisms with advantagious variations survive and continue with the generation while those with disadvantagious various migrate or die.
Question 5
The figure below shows the parts of the human digestive system. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

a) Name the organs labelled A, B and D.
A
B
D
b) State the role of part labelled C
c) Name the two salivary glands in human beings.
d) Give two adaptations of part labelled D to its function.
Answer
a)
A - Gall blader
B - Liver
D - Ileum
b) - Secretion of hormone, insulin and glycogen
- Secretion of pancreatic juice / digestive enzyme eg typsin
c) - Sublinguals
- Parotid
d) - Long to increase surface area for absorption of food.
- Highly coiled to reduce the movement of digested food allowing more time for absorption.
B - Liver
D - Ileum
b) - Secretion of hormone, insulin and glycogen
- Secretion of pancreatic juice / digestive enzyme eg typsin
c) - Sublinguals
- Parotid
d) - Long to increase surface area for absorption of food.
- Highly coiled to reduce the movement of digested food allowing more time for absorption.
