Question 1
A potted plant was placed in each of the following conditions for a period of one hour in the order given and transpiration in each hour was measured. The air temperature was 180C throughout the experiment.
| Conditions | Relative Humidity | Transpiration g/hr |
|---|---|---|
| A) Still air in sunlight and shade | 70 | 1.2 |
| B) Moving air only | 70 | 1.6 |
| C) Still air in bright sunlight | 70 | 3.75 |
| D) Still air in dark chamber | 70 | 0.20 |
- Account for the rate of transpiration in
i. Condition C
ii. Condition D - Name the apparatus used to measure the rate of transpiration
- Give one modification in the stomata of xerophytes that reduce the rate of transpiration
Answer
-
i. Condition C - There is highest rate of transpiration; because of high light intensity hence the stomata are fully opened; bright light increases the internal leaf temperature hence high rate of evaporation of water.
ii. Condition D - There is lowest rate of transpiration; because there was high relative humidity hence a low saturation deficit; there was no light hence stomata are closed. - Potometer
- Fewer number of stomata
Question 2
Sickle cell anaemia is a disease in which people produce abnormal haemoglobin in their red blood cells. Letter H represents the gene for normal haemoglobin while letter S represent the gene for abnormal haemoglobin. Heterozygous individuals are said to have sickle cell trait.
- If both parents have sickle cell trait, work out the proportion of their offspring that have sickle cell anemia.
- Explain why sickle cell trait is more prevalent in tropical countries than temperate countries.
- Name any other disease caused by gene mutation.
Answer
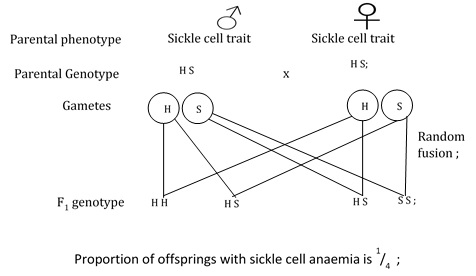
- In tropical countries, malaria is more prevalent; people with sickle cell trait are more resistant to malaria than normal individuals because plasmodium survive very poorly in sickled red blood cells.
- Haemophilia
Question 3
Equal volumes of three different sugar solutions were placed in visking tubings X, Y and Z. The tubings were placed in a beaker containing 5%sugar solution. The set up was left for two hours. The results were as shown in the diagram below.
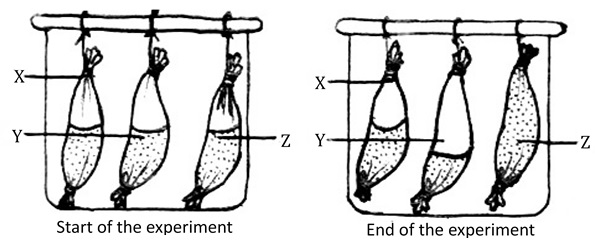
- Name the process being investigated.
- What is the significance of set up X in the experiment?
- Account for the observations in set up Y and Z
Y
Z - Name a structure in cells that can be compared to the visking tubing.
- Explain how high temperature above 400C will affect the process being investigated in the cells of organism.
Answer
- Osmosis
- A control experiment
-
Y - Solution Y is hypotonic to the 5% sugar solution in the beaker; it loses water by osmosis to the solution in the beaker; decreasing in volume.
Z - Solution Z is hypertonic to the 5% sugar solution; it draws in water by osmosis from the beaker; hence increasing in volume. - Cell membrane
- The process stops as high temperature destroys the structure of the cell membrane.
Question 4
The diagrams below show changes in the life cycle of a flowering plant.
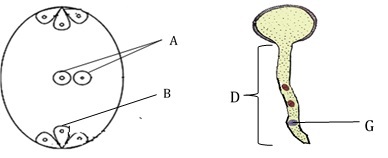
- Name the parts labelled A, B and G.
A
B
G - State the function of the part labelled D
- i. What will part A develop into after fertilization
ii. Define the term parthenocarpy
Answer
-
A - Polar nuclei
B - Egg cell
G - Tube nucleus - Transport male gametes to the embryo sac for double fertilization to occur
- i. Endosperm
ii. Parthenocarpy - development of a fruit without fertilization.
Question 5
Name two features in flowering plants that prevent self-fertilization.
Answer
a) Heterostyly
b) Protandry
b) Protandry
