Common sources of current electricity include dry cells, car batteries, bicycle dynamos, petrol-driven generators, diesel-driven generators, wind-driven generators, hydro-electric generators and solar panels.
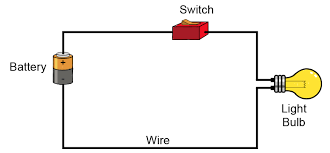
a) Dry cells (Torch battery)
- Dry cells have a positive (+) terminal and a negative (_) terminal.They contain chemicals which produce electricity. Two or more dry cells connected together make up battery.
- Dry cells are used in clocks, torches, radios among other appliances.
b) Car battery
- A car battery produces electricity from liquid chemicals. It has a positive and negative terminal. It is made up of six cells.
- It is used for powering motor vehicles, for lighting houses and for operating radios and televisions.

c) Bicycle dynamo
- A bicycle dynamo is a small generator that produces small amounts of electricity.
- The electricity is produced when a moving wheel of a bicycle rotates the knobs of the dynamo. The electricity generated provides light for the cyclist at night.
d)Petrol and diesel-driven generators
- These are large generators that use petrol or diesel-driven engines. They rotate machines that produce electricity.
- These generators are used to generate energy used to power important equipment in hospitals, factories and schools.
- They are useful in areas where there is no electricity.
e) Geothermal generators.
- These are large generators that produce large amounts of electricity.
- Geothermal generators use steam under pressure to produce electricity.
f) Hydro-electric generators
- These are large generators that produce large amounts of electricity from water.
- In hydro-electric generating stations, water flowing at a high speed from a waterfall or dam rotates a turbine which in turn drives a generator that produces electricity.
- This electricity is then directed into electric wires that carry it to homes, schools and factories for use.
g) Wind-driven turbines
- These are large turbines connected to generators that produce large amount of electricity.
- A wind-driven fan rotates a turbine connected to a machine that produces electricity.

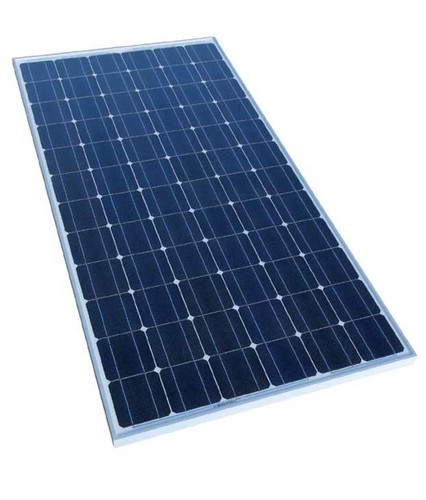
h) Solar panels
These are light-sensitive cells that change light energy from the sun to electricity which is stored in batteries or used to power electrical appliances.