- A parasite is an organism that fully depends on another organism for its survival.
- The organism that is depended on is called a host.
- Parasites also called pests , depend on the host for food.
- Livestock parasites fall under two categories: external and internal parasites.
- Parasites that live on the skin of an animal are called external parasites.
- Examples of external parasites are ticks, fleas, tsetse-fly, mites and lice.

- Ticks attack cattle, sheep, goats, poultry, camels, horses, pigs and rabbits.
- Fleas attack cattle, sheep, poultry, camels, horses, pigs and horses.
- Tsetse flies attack all domestic animals.
- Parasites that live inside the host are called internal parasites.
- Examples of internal parasites include roundworms, tapeworms, liver flukes, hookworms and lungworms.
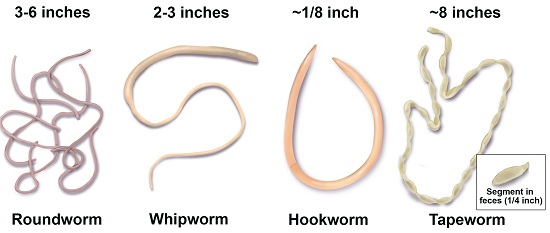
- Roundworms attack cattle, sheep, goats and fish. They are found in the liver, lungs and small intestines.
- Tapeworms attack cattle, sheep, goats and pigs and are found in the small intestines and liver.
- Liver flukes attack cattle, sheep, goats and pigs and are found in the lungs and the liver.
- Hookworms attack sheep and goats. They are found in the small intestines.
- Lungworms attack cattle, sheep goats and pigs. They are found in the brain, stomach and lungs.