- Immunization is the administration or giving of vaccines to a person so as to prevent a disease.
- The administered medicine is called the
vaccine, and the process is called
vaccination or
immunization.
- When the vaccine is introduced into the body, it improves the
immune system of the person against the disease.
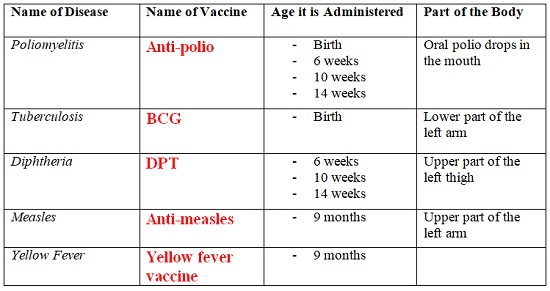
- Some of the immunizable diseases include;
tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, measles, diphtheria, whooping cough and
tetanus.
- The vaccine may be given as an injection, or through the mouth.
- The following table is a summary of vaccines given to infants