1. It enable the country to get access to wider range/variety of goods and services from other countries.
2. It enable the country to get what it does not produce.
3. It helps in promoting peace among the trading countries.
4. It enable the country to specialize in it’s production activities where they feel they have an advantage.
5. It earns the country revenue through taxes and licenses fees paid by the importers and exporters in the country.
6. It enable the country to dispose of its surplus goods and services thereby avoiding wastage.
7. It creates employment opportunities to the citizens of that country either directly or indirectly 8. It may lead to the development of the country through importation of capital goods in to the country.
9. It encourages easy movement of factors of production across the boarders of the countries involved.
10. It enable countries to earn foreign exchange which it can use to pay for its imports.
11. A country may be able to obtain goods and services cheaply than if they have been produced locally.
12. During hard times or calamities such as wars, the country is able to get assistance from the trading partners.
13. It brings about competition between the imported and locally produced goods, leading to improvement in their quality.
14. It gives the country an opportunity to exploit fully its natural resources, due to increased market.
Disadvantages of International trade
1. It may lead to collapse of the local industries, as people will tend to go for the imported goods. The collapse may also lead to loss of employment.
2. It may also lead to importation of harmful foods and services such as drugs and pornographic materials.
3. May lead to over depending on imported commodities especially the essential ones, making the country to be a slave of the other countries, interfering with their sovereignty.
4. It may make the country to suffered during emergencies if they mainly rely on the imported goods.
5. May make the country to suffer from import inflation.
6. May lead to acquisition of bad culture from other countries as a result of their interactions.
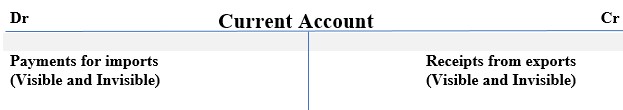
7. May lead to unfavorable balance of payment, if the import is higher than exports. This refers to the rate at which the country’s export exchanges with those from other country. That is:
Terms of Trade
- This refers to the rate at which the country’s export exchanges with those from other country. That is:This refers to the rate at which the country’s export exchanges with those from other country. That is:
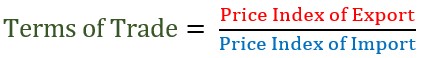
- Favourable terms of trade will make the country spent little on import and gain a lot of foreign exchange from other countries.
For example
Then table below shows trade between Kenya and China in the year 2004 and 2005, with the Kenyan government exporting and importing to and from china, and China also importing and Exporting from and to Kenya.
| Average prices of export | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Kenya | China |
| 2004 | 1000 | 4000 |
| 2005 | 1200 | 6500 |
Calculate the Terms of trade for Kenya
Factors that may lead to either favourable or unfavourable terms of trade
- The country is experiencing a favourable terms of trade if:
- The prices of imports decline and those of export remains the constant.
- The prices of imports declines while those of exports increase.
- The price of imports remains constant while those of exports increase.
- The prices of import and export increases but the rate of increase in export is higher.
- Both prices decrease but the decrease in import prices is higher.
- Prices of import increases while those of exports decline.
- Prices of import remains constant while those of export declines.
- Prices of import increase as the export remains constant.
- Both prices increase, but for imports increases at a higher rate than export.
- Both prices decrease, but for export decreases at a higher rate than import.
- The terms of trade may differ due to:
1. The nature of the commodity being exported. If a country exports raw materials, or unprocessed agricultural products, its terms of trade will be unfavourable, as compared to a country that exports manufactured goods.
2. Nature of the commodity being imported. A country that imports manufactured goods is likely to have unfavourable terms of trade as compared to that which imports raw materials or agricultural produce.
3. Change in demand for a country’s export. An increase in demand for the country’s export at the world market will make it have favourable terms of trade as compared to those with low demand at the world market.
4. Existing of world economic order favouring the products from more developed countries. This may make the developing countries to have deteriorating terms of trade.
5. Total quantity supplied. A country exporting what most countries are exporting will have their products trading at a lower price, experiencing unfavourable terms of trade as compared to a country that export what only few countries export.
6. Trade restrictions by trading partners. A country with no trading restrictions is likely to import more products, leading to unfavourable terms of trade, as compared to if it impose trade restrictions.