Whole Life Assurance
In whole life assurance, the assured pays regular premiums until he/she dies. The sum assured is payable to the beneficiaries upon the death of the assured.
Whole life assurance covers disabilities due to illness or accidents i.e. if the insured is disabled during the life of the policy due to illness or accidents, the insurer will pay him/her for the income lost.
Endowment policy/insurance
This is whereby the insured pays regular premiums over a specified period of time. The sum assured is payable either at the expiry of the period (maturity of policy) or on death of the insured, whichever comes first.
The insured, at expiry of policy is given the total sum assured to use for activities of his own choice.(ordinary endowment policy). Where the insured dies before maturity of contract, the beneficiaries are given these amounts
The assured person may be paid a certain percentage of the sum assured at intervals until the expiry of the policy according to the terms of contract. Such an arrangement is known as
Anticipated Endownment policy.
Advantages of Endowment policies
- They are a form of saving by the insured, for future investments.
- Premiums are payable over a specified period of time which can be determined to suit his/her needs e.g. retirement time.
- Where the assured lives and time policy matures, he receives the value of sum assured.
- Policy can be used as security for loans from financial institutions.
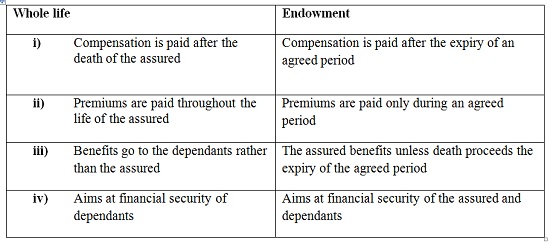
Differences Between a whole life policy and an Endowment policy
Term insurance
The insured here covers his life against death for a given time period e.g. 1yr, 5yrs e.t.c.
If the policyholder dies within this period, his/her dependants are compensated.
If the insured does not die within this specified period, there is no compensation. However, a renewal can be taken.
Education plan/policies
This policy is normally taken by parents for their children’s future educational needs. The policy gives details of when the payments are due.
Statutory schemes
The Government offers some types of insurance schemes which are aimed at improving/providing welfare to the members of the scheme such as medical services and retirement benefits. A member and the employer contribute, at regular intervals, certain amounts of money towards the scheme. Examples include NHIF, NSSF, and Widows and children pension scheme.
