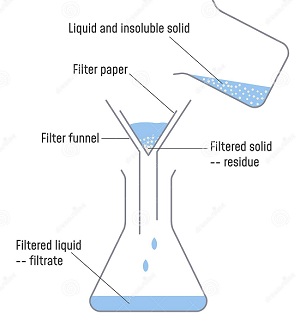
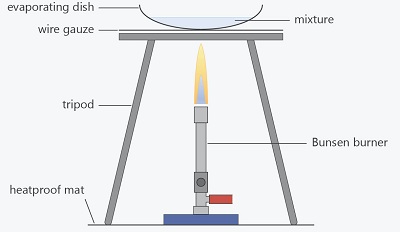
- A mixture is a combination of two or more substances. Examples of mixture include soil and air.
- Mixtures can be made by mixing solids and liquids, solids and solids or liquids and liquids.
- A solid that dissolves in a liquid is called a solute.
- A liquid that dissolves a solute is called a solvent.
- A solute and a solvent make a solution.
- The following are examples of solutes, solvents and solutions respectively
- Salt + Water → Salt Solution
- Sugar + Water → Sugar Solution
- Glucose + Water → Glucose Solution
- Size of the particles of the solute.
- The amount of the solvent.
- The temperature of the solvent
- Stirring of the mixture.
- Liquids that mix with other liquids are called miscible liquids.
- Liquids that do not mix are called immiscible liquids.
The following are examples of miscible and immiscible liquids.
- Miscible Liquids: water and milk, cooking oil and paraffin, methylated spirit and milk, petrol and turpentine
- Immiscible Liquids: water and cooking oil, kerosene and water, engine oil and milk, turpentine and ink.