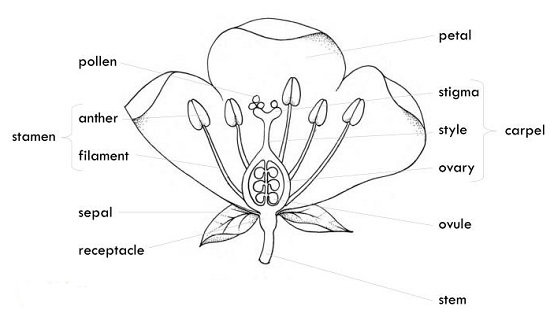
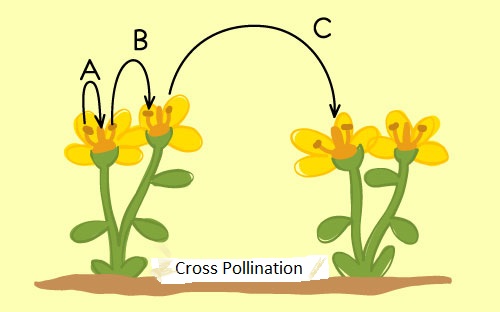
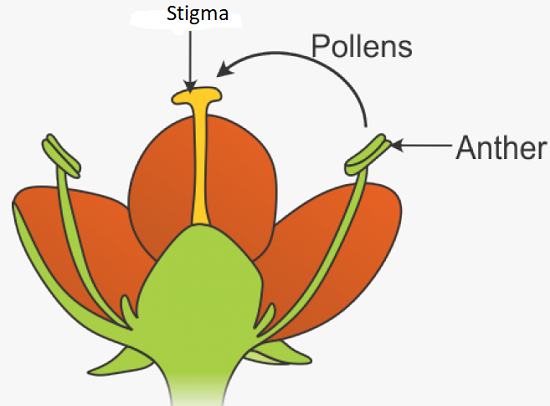
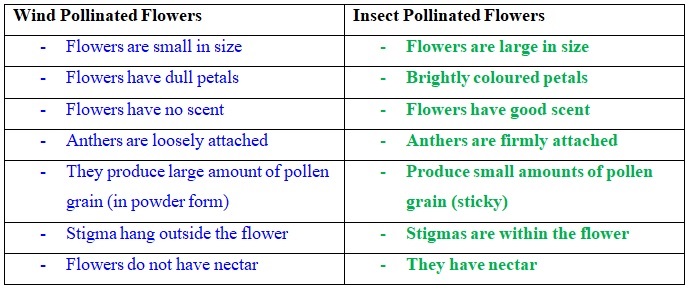
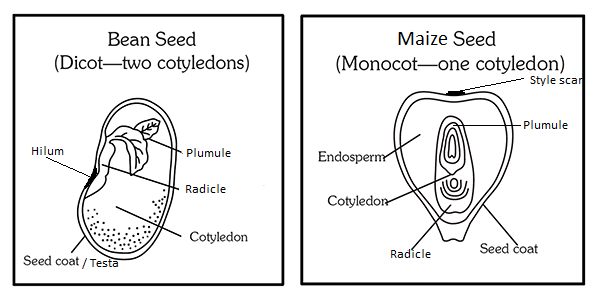
Germination occurs when a seed starts developing into a plant.
- In order for a seed to germinate, it needs
water, oxygen and warmth.
- Water dissolves the food in the cotyledon or endosperm.
- Oxygen is needed for respiration, which provides the energy needed for the seed to grow.
- Warmth makes the developing cells active.
Water in Germination
- To show that water is needed for germination, one can use the following experiment.
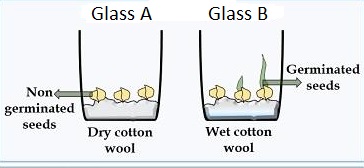
- There was germination in B and not in A because A doies not have water and B has water.
Oxygen in Germination
- To show that oxygen is needed for germination, one can use the following experiment.
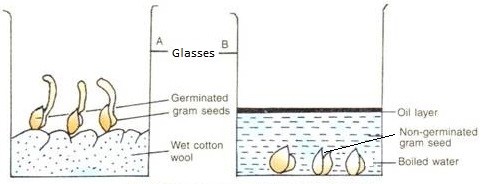
- There was germination in B and not in A, because B does no have oxygen.
- When water has been boiled, oxygen is removed and oil prevents any oxygen from from dissolving into the water.
Warmth in Germination
- To show that warmth is needed for germination, one can use the following experiment.
- Seed are put in two glasses with wet cotton wool
- One of the glasses is then dipped in a bigger container filled with ice.
- Germination occurs in the beaker that has NOT been dipped in ice, and not in the other one in ice.
- This is because the ice crystals lower temperature and remove warmth, making it hard for seeds to germinate.